Down selecting adjuvanted vaccine formulations: a comparative method for harmonized evaluation
- PMID: 29386070
- PMCID: PMC5793412
- DOI: 10.1186/s12865-018-0245-0
Down selecting adjuvanted vaccine formulations: a comparative method for harmonized evaluation
Abstract
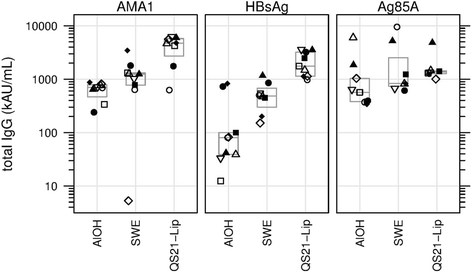
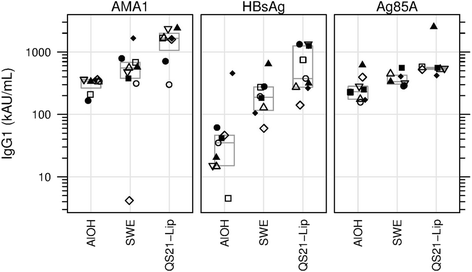
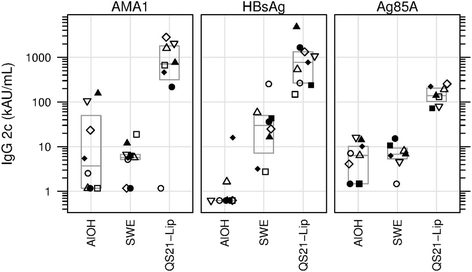
Background: The need for rapid and accurate comparison of panels of adjuvanted vaccine formulations and subsequent rational down selection, presents several challenges for modern vaccine development. Here we describe a method which may enable vaccine and adjuvant developers to compare antigen/adjuvant combinations in a harmonized fashion. Three reference antigens: Plasmodium falciparum apical membrane antigen 1 (AMA1), hepatitis B virus surface antigen (HBsAg), and Mycobacterium tuberculosis antigen 85A (Ag85A), were selected as model antigens and were each formulated with three adjuvants: aluminium oxyhydroxide, squalene-in-water emulsion, and a liposome formulation mixed with the purified saponin fraction QS21.
Results: The nine antigen/adjuvant formulations were assessed for stability and immunogenicity in mice in order to provide benchmarks against which other formulations could be compared, in order to assist subsequent down selection of adjuvanted vaccines. Furthermore, mouse cellular immune responses were analyzed by measuring IFN-γ and IL-5 production in splenocytes by ELISPOT, and humoral responses were determined by antigen-specific ELISA, where levels of total IgG, IgG1, IgG2b and IgG2c in serum samples were determined.
Conclusions: The reference antigens and adjuvants described in this study, which span a spectrum of immune responses, are of potential use as tools to act as points of reference in vaccine development studies. The harmonized methodology described herein may be used as a tool for adjuvant/antigen comparison studies.
Keywords: AMA1; Adjuvants; Ag85A; Aluminium oxyhydroxide; HBsAg; Hepatitis B; Plasmodium falciparum; QS21; Squalene-in-water SWE; Tuberculosis.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors’ information
SYY, VS, NW, CK and ER are employees of Biomedical Primate Research Centre, The Netherlands. CB, SH, LB and NC are employees of the Vaccine Formulation Laboratory, University of Lausanne, Switzerland. PD is self-employed. MF is an employee of WHO, Switzerland.
Ethics approval
All animal work was performed under the guidelines of Biomedical Primate Research Centre (BPRC) which uses protocols conforming to European animal welfare regulations. The independent ethics committee at BPRC, constituted according to Dutch law on animal experiments, approved the study protocol (number DEC 658) prior to start of the experiment.
Consent for publication
Not Applicable.
Competing interests
Authors declare no competing financial interests. SYY, VS, NW, CK and ER are employees of Biomedical Primate Research Centre, The Netherlands. CB, SH, LB and NC are employees of the Vaccine Formulation Laboratory, University of Lausanne, Switzerland. PD is self-employed. MF is an employee of WHO, Switzerland.
Figures



References
-
- Kawano Y, Noma T, Yata J. Regulation of human IgG subclass production by cytokines. IFN-gamma and IL-6 act antagonistically in the induction of human IgG1 but additively in the induction of IgG2. J Immunol. 1994;153(11):4948–4958. - PubMed
-
- Mizoguchi C, et al. IL-5 induces IgG1 isotype switch recombination in mouse CD38-activated sIgD-positive B lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1999;162(5):2812–2819. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

