Modeling Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia and Testing Interventions for Adrenal Insufficiency Using Donor-Specific Reprogrammed Cells
- PMID: 29386111
- PMCID: PMC5809617
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2018.01.003
Modeling Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia and Testing Interventions for Adrenal Insufficiency Using Donor-Specific Reprogrammed Cells
Abstract
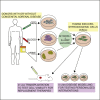
Adrenal insufficiency is managed by hormone replacement therapy, which is far from optimal; the ability to generate functional steroidogenic cells would offer a unique opportunity for a curative approach to restoring the complex feedback regulation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis. Here, we generated human induced steroidogenic cells (hiSCs) from fibroblasts, blood-, and urine-derived cells through forced expression of steroidogenic factor-1 and activation of the PKA and LHRH pathways. hiSCs had ultrastructural features resembling steroid-secreting cells, expressed steroidogenic enzymes, and secreted steroid hormones in response to stimuli. hiSCs were viable when transplanted into the mouse kidney capsule and intra-adrenal. Importantly, the hypocortisolism of hiSCs derived from patients with adrenal insufficiency due to congenital adrenal hyperplasia was rescued by expressing the wild-type version of the defective disease-causing enzymes. Our study provides an effective tool with many potential applications for studying adrenal pathobiology in a personalized manner and opens venues for the development of precision therapies.
Keywords: NR5A1; adrenal cortex; adrenal insufficiency; congenital adrenal hyperplasia; disease modeling; reprogramming; steroidogenic cells; steroidogenic factor 1; transplantation; urine-derived stem cells.
Copyright © 2018 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures




References
-
- Achermann J.C., Meeks J.J., Jameson J.L. Phenotypic spectrum of mutations in DAX-1 and SF-1. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2001;185:17–25. - PubMed
-
- Bergthorsdottir R., Leonsson-Zachrisson M., Odén A., Johannsson G. Premature mortality in patients with Addison’s disease: a population-based study. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2006;91:4849–4853. - PubMed
-
- Bharadwaj S., Liu G., Shi Y., Wu R., Yang B., He T., Fan Y., Lu X., Zhou X., Liu H. Multipotential differentiation of human urine-derived stem cells: potential for therapeutic applications in urology. Stem Cells. 2013;31:1840–1856. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

