Nonlinear mixed-modelling discriminates the effect of chemicals and their mixtures on zebrafish behavior
- PMID: 29386525
- PMCID: PMC5792435
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-20112-x
Nonlinear mixed-modelling discriminates the effect of chemicals and their mixtures on zebrafish behavior
Abstract
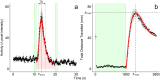
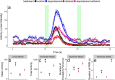
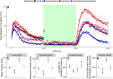
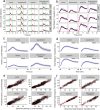
Zebrafish (Danio rerio) early-life stage behavior has the potential for high-throughput screening of neurotoxic environmental contaminants. However, zebrafish embryo and larval behavioral assessments typically utilize linear analyses of mean activity that may not capture the complexity of the behavioral response. Here we tested the hypothesis that nonlinear mixed-modelling of zebrafish embryo and larval behavior provides a better assessment of the impact of chemicals and their mixtures. We demonstrate that zebrafish embryo photomotor responses (PMRs) and larval light/dark locomotor activities can be fit by asymmetric Lorentzian and Ricker-beta functions, respectively, which estimate the magnitude of activity (e.g., maximum and total activities) and temporal aspects (e.g., duration of the responses and its excitatory periods) characterizing early life-stage zebrafish behavior. We exposed zebrafish embryos and larvae to neuroactive chemicals, including isoproterenol, serotonin, and ethanol, as well as their mixtures, to assess the feasibility of using the nonlinear mixed-modelling to assess behavioral modulation. Exposure to chemicals led to distinct effects on specific behavioral characteristics, and interactive effects on temporal characteristics of the behavioral response that were overlooked by the linear analyses of mean activity. Overall, nonlinear mixed-modelling is a more comprehensive approach for screening the impact of chemicals and chemical mixtures on zebrafish behavior.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Nagel R. DarT: the embryo test with the zebrafish Danio rerio – a general model in ecotoxicology and toxicology. ALTEX-Altern Tierexp. 2002;19:38–38. - PubMed
-
- Thompson, W. A., Arnold, V. I. & Vijayan, M. M. Venlafaxine in embryos stimulates neurogenesis and disrupts larval behavior in zebrafish. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 10.1021/acs.est.7b04099. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

