Thyroid stimulating hormone stimulates the expression of glucose transporter 2 via its receptor in pancreatic β cell line, INS-1 cells
- PMID: 29386586
- PMCID: PMC5792451
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-20449-3
Thyroid stimulating hormone stimulates the expression of glucose transporter 2 via its receptor in pancreatic β cell line, INS-1 cells
Abstract
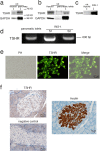
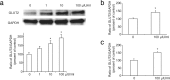
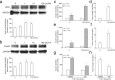
Thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) stimulates the secretion of thyroid hormones by binding the TSH receptor (TSHR). TSHR is well-known to be expressed in thyroid tissue, excepting it, TSHR has also been expressed in many other tissues. In this study, we have examined the expression of TSHR in rat pancreatic islets and evaluated the role of TSH in regulating pancreas-specific gene expression. TSHR was confirmed to be expressed in rodent pancreatic islets and its cell line, INS-1 cells. TSH directly affected the glucose uptake in INS cells by up-regulating the expression of GLUT2, and furthermore this process was blocked by SB203580, the specific inhibitor of the p38 MAPK signaling pathway. Similarly, TSH stimulated GLUT2 promoter activity, while both a dominant-negative p38MAPK α isoform (p38MAPK α-DN) and the specific inhibitor for p38MAPK α abolished the stimulatory effect of TSH on GLUT2 promoter activity. Finally, INS-1 cells treated with TSH showed increased protein level of glucokinase and enhanced glucose-stimulated insulin secretion. Together, these results confirm that TSHR is expressed in INS-1 cells and rat pancreatic islets, and suggest that activation of the p38MAPK α might be required for TSH-induced GLUT2 gene transcription in pancreatic β cells.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Octanoic acid potentiates glucose-stimulated insulin secretion and expression of glucokinase through the olfactory receptor in pancreatic β-cells.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018 Sep 3;503(1):278-284. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.06.015. Epub 2018 Jun 11. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018. PMID: 29885841
-
The Adverse Effects of Thyrotropin Absence on Pancreatic β Cell Function in Mice.J Diabetes Res. 2019 Apr 15;2019:9536032. doi: 10.1155/2019/9536032. eCollection 2019. J Diabetes Res. 2019. PMID: 31179344 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of TNF-α on the expression of ABCA1 in pancreatic β-cells.J Mol Endocrinol. 2018 Oct 15;61(4):185-193. doi: 10.1530/JME-18-0167. J Mol Endocrinol. 2018. PMID: 30131353
-
Transcriptional regulation of glucose sensors in pancreatic beta cells and liver.Curr Diabetes Rev. 2006 Feb;2(1):11-8. doi: 10.2174/157339906775473581. Curr Diabetes Rev. 2006. PMID: 18220613 Review.
-
β-Arrestin 1 in Thyrotropin Receptor Signaling in Bone: Studies in Osteoblast-Like Cells.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2020 May 20;11:312. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2020.00312. eCollection 2020. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2020. PMID: 32508750 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Relationship between the Central and Peripheral Thyroid Sensitivity Indices and Fetal Macrosomia: A Cohort Study of Euthyroid Pregnant Women in China.Diagnostics (Basel). 2023 Jun 9;13(12):2013. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics13122013. Diagnostics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37370908 Free PMC article.
-
Free triiodothyronine (FT3)-to-free thyroxine (FT4) ratio identified as a risk factor for gestational diabetes in euthyroid pregnant women: insights from a Chinese population cohort study.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Nov 20;14:1281285. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1281285. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 38053730 Free PMC article.
-
Radioactive Iodine-131 Therapy Reduced the Risk of MACEs and All-Cause Mortality in Elderly with Hyperthyroidism Combined with Type 2 Diabetes.Int J Gen Med. 2024 Sep 21;17:4281-4295. doi: 10.2147/IJGM.S484910. eCollection 2024. Int J Gen Med. 2024. PMID: 39324146 Free PMC article.
-
Impaired Glucose Metabolism, Anti-Diabetes Medications, and Risk of Thyroid Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Jan 22;14(3):555. doi: 10.3390/cancers14030555. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35158824 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transcriptomic and Quantitative Proteomic Profiling Reveals Signaling Pathways Critical for Pancreatic Islet Maturation.Endocrinology. 2020 Dec 1;161(12):bqaa187. doi: 10.1210/endocr/bqaa187. Endocrinology. 2020. PMID: 33053583 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

