Effectiveness of stevia as a mouthrinse among 12-15-year-old schoolchildren in Nellore district, Andhra Pradesh - A randomized controlled trial
- PMID: 29386799
- PMCID: PMC5767988
- DOI: 10.4103/jisp.jisp_54_17
Effectiveness of stevia as a mouthrinse among 12-15-year-old schoolchildren in Nellore district, Andhra Pradesh - A randomized controlled trial
Abstract
Aim: The aim of this study is to determine the effectiveness of stevia as a daily mouthrinse among 12-15 year-old schoolchildren in Nellore District, Andhra Pradesh.
Materials and methods: A randomized, controlled triple blind trial was carried out among 108 children in B. V. S Municipallity Girls High school in Nellore. Children were randomly allocated into four groups comprising 27 in each group. Four mouthrinses composed of 0.2% chlorhexidine gluconate; 0.05% sodium fluoride, 10.6% stevioside and placebo were provided to the study participants. Plaque index, gingival index, and International Caries Detection and Assessment System (ICDAS) II, respectively, were used for assessing oral condition. The mouthrinsing was carried out for 6 months.
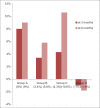
Results: Group C showed maximum reduction of 8% and 10% on plaque and gingival scores, respectively, followed by Group A and Group B. However, Group D participants showed 1.5% and 1.8% increase in plaque and gingival scores, respectively. Analysis of ICDAS scores at 6 months indicated that values recorded were same as baseline for all the three groups except that for Group D, there was an increase in the prevalence of cavitated lesion D2-6from 5.6% to 5.8%.
Conclusion: Stevia demonstrated very potent antiplaque and antigingivitis properties as compared to other mouthrinses at the end of 6 months trial.
Keywords: Antigingivitis; antiplaque; mouthrinse.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Mandel ID. Chemotherapeutic agents for controlling plaque and gingivitis. J Clin Periodontol. 1988;15:488–98. - PubMed
-
- Zanela NL, Bijella MF, Rosa OP. The influence of mouthrinses with antimicrobial solutions on the inhibition of dental plaque and on the levels of mutans streptococci in children. Pesqui Odontol Bras. 2002;16:101–6. - PubMed
-
- Slavutzky SM. Stevia and sucrose effect on plaque formation. J Verbr Lebensm. 2010;5:213–6.
-
- Silness J, Loe H. Periodontal disease in pregnancy. II. Correlation between oral hygiene and periodontal condition. Acta Odontol Scand. 1964;22:121–35. - PubMed
-
- Loe H, Silness J. Periodontal disease in pregnancy. I. Prevalence and severity. Acta Odontol Scand. 1963;21:533–51. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources