Trigeminal schwannoma
- PMID: 29386819
- PMCID: PMC5773990
- DOI: 10.4103/njms.NJMS_82_14
Trigeminal schwannoma
Abstract
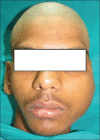
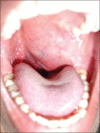
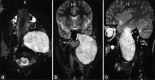
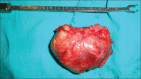
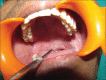
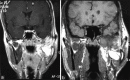
Schwannoma is a benign tumor of the nerve sheath arising from the perineural schwann cells. The nerves most commonly involved in schwannomas of the head and neck are the vagus and the cervical sympathetic chain. Trigeminal schwannomas are rare tumours. A 17 year old male patient with a chief complaint of swelling on face was diagnosed as suffering from bening tumor extending from cranial base (from foramen ovale) to the parapharengeal space. Mandibular access osteotomy was done to expose the tumor. Surgical excision of the tumor was done along with the preservation of the nerve. Schwannomas can occur along the pathway of any somatic or sympathetic nerve. Superficial schwannomas require simple exposure and excision but the one which are deep and large, may require complex access osteotomies. Careful surgery is required to preserve the nerve function. Once completely excised, the prognosis is excellent.
Keywords: Access osteotomy; schwannoma; trigeminal nerve.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Argenyi ZB, Cooper PH, Santa Cruz D. Plexiform and other unusual variants of palisaded encapsulated neuroma. J Cutan Pathol. 1993;20:34–9. - PubMed
-
- MacCollin M, Woodfin W, Kronn D, Short MP. Schwannomatosis: A clinical and pathologic study. Neurology. 1996;46:1072–9. - PubMed
-
- Saydam L, Kizilay A, Kalcioglu T, Gurer I. Ancient cervical vagal neurilemmoma: A case report. Am J Otolaryngol. 2000;21:61–4. - PubMed
-
- Redman RS, Guccion JG, Spector CJ, Keegan BP. Cellular schwannoma of the mandible: A case report with ultrastructural and immunohistochemical observations. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1996;54:339–44. - PubMed
-
- Hatziotia JC, Asprides H. Neurilemoma (schwannoma) or the oral cavity. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1967;24:510–26. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

