Gene Expression Analysis Reveals Novel Shared Gene Signatures and Candidate Molecular Mechanisms between Pemphigus and Systemic Lupus Erythematosus in CD4+ T Cells
- PMID: 29387060
- PMCID: PMC5776326
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.01992
Gene Expression Analysis Reveals Novel Shared Gene Signatures and Candidate Molecular Mechanisms between Pemphigus and Systemic Lupus Erythematosus in CD4+ T Cells
Abstract
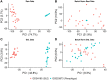
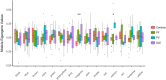
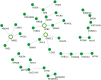
Pemphigus and systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) are severe potentially life-threatening autoimmune diseases. They are classified as B-cell-mediated autoimmune diseases, both depending on autoreactive CD4+ T lymphocytes to modulate the autoimmune B-cell response. Despite the reported association of pemphigus and SLE, the molecular mechanisms underlying their comorbidity remain unknown. Weighted gene co-expression network analysis (WGCNA) of publicly available microarray datasets of CD4+ T cells was performed, to identify shared gene expression signatures and putative overlapping biological molecular mechanisms between pemphigus and SLE. Using WGCNA, we identified 3,280 genes co-expressed genes and 14 co-expressed gene clusters, from which one was significantly upregulated for both diseases. The pathways associated with this module include type-1 interferon gamma and defense response to viruses. Network-based meta-analysis identified RSAD2 to be the most highly ranked hub gene. By associating the modular genes with genome-wide association studies (GWASs) for pemphigus and SLE, we characterized IRF8 and STAT1 as key regulatory genes. Collectively, in this in silico study, we identify novel candidate genetic markers and pathways in CD4+ T cells that are shared between pemphigus and SLE, which in turn may facilitate the identification of novel therapeutic targets in these diseases.
Keywords: CD4+ T cells; autoimmunity; gene expression analysis; pemphigus; systemic lupus erythematosus; weighted gene co-expression analysis.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Exploration of the Shared Gene Signatures and Molecular Mechanisms Between Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension: Evidence From Transcriptome Data.Front Immunol. 2021 Jul 15;12:658341. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.658341. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34335565 Free PMC article.
-
Identifying key genes in CD4+ T cells of systemic lupus erythematosus by integrated bioinformatics analysis.Front Genet. 2022 Aug 15;13:941221. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.941221. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 36046235 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of the shared genes and immune signatures between systemic lupus erythematosus and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.Hereditas. 2023 Mar 4;160(1):9. doi: 10.1186/s41065-023-00270-3. Hereditas. 2023. PMID: 36871016 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of STAT Signaling Pathways in the Pathogenesis of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus.Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2017 Apr;52(2):164-181. doi: 10.1007/s12016-016-8550-y. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2017. PMID: 27216430 Review.
-
Regulatory T cells in systemic lupus erythematosus.Eur J Immunol. 2015 Feb;45(2):344-55. doi: 10.1002/eji.201344280. Epub 2014 Dec 15. Eur J Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25378177 Review.
Cited by
-
Weighted gene co-expression network analysis revealed key biomarkers associated with the diagnosis of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy.Hereditas. 2020 Oct 24;157(1):42. doi: 10.1186/s41065-020-00155-9. Hereditas. 2020. PMID: 33099311 Free PMC article.
-
TRIM5 Promotes Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Through CD4(+) T Cells and Macrophage.Int J Gen Med. 2023 Aug 18;16:3567-3580. doi: 10.2147/IJGM.S416493. eCollection 2023. Int J Gen Med. 2023. PMID: 37614552 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic effect of Bacillus Calmette-Guerin polysaccharide nucleic acid on mast cell at the transcriptional level.PeerJ. 2019 Aug 21;7:e7404. doi: 10.7717/peerj.7404. eCollection 2019. PeerJ. 2019. PMID: 31497384 Free PMC article.
-
Gene expression profiling meta-analysis reveals novel gene signatures and pathways shared between tuberculosis and rheumatoid arthritis.PLoS One. 2019 Mar 7;14(3):e0213470. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0213470. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 30845171 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of novel biomarkers for lupus nephritis.Biomol Biomed. 2025 Jan 14;25(2):406-424. doi: 10.17305/bb.2024.10450. Biomol Biomed. 2025. PMID: 38980684 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

