An immune-modulating formula comprising whey peptides and fermented milk improves inflammation-related remote organ injuries in diet-induced acute pancreatitis in mice
- PMID: 29387516
- PMCID: PMC5787410
- DOI: 10.12938/bmfh.17-011
An immune-modulating formula comprising whey peptides and fermented milk improves inflammation-related remote organ injuries in diet-induced acute pancreatitis in mice
Abstract
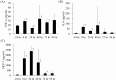
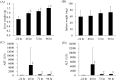
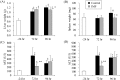
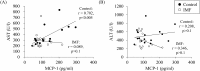
It has been demonstrated that an immune-modulating enteral formula enriched with whey peptides and fermented milk (IMF) had anti-inflammatory effects in some experimental models when it was administered before the induction of inflammation. Here, we investigated the anti-inflammatory effects of the IMF administration after the onset of systemic inflammation and investigated whether the IMF could improve the remote organ injuries in an acute pancreatitis (AP) model. Mice were fasted for 12 hours and then fed a choline-deficient and ethionine-supplemented diet (CDE diet) for 24 hours to induce pancreatitis. In experiment 1, the diet was replaced with a control enteral formula, and mice were sacrificed at 24-hour intervals for 96 hours. In experiment 2, mice were randomized into control and IMF groups and received the control formula or the IMF respectively for 72 hr or 96 hr. In experiment 1, pancreatitis was induced by the CDE diet, and inflammatory mediators were elevated for several days. Remote organ injuries such as splenomegaly, hepatomegaly, and elevation of the hepatic enzymes developed. A significant strong positive correlation was observed between plasma MCP-1 and hepatic enzymes. In experiment 2, the IMF significantly improved splenomegaly, hepatomegaly, and the elevation of hepatic enzymes. Plasma MCP-1 levels were significantly lower in the IMF group than in the control group. Nutrition management with the IMF may be useful for alleviating remote organ injuries after AP.
Keywords: acute pancreatitis; immune-modulating formula; inflammation; remote organ injury.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Nutritional treatment with an immune-modulating enteral formula alleviates 5-fluorouracil-induced adverse effects in rats.PLoS One. 2019 Nov 26;14(11):e0225389. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0225389. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31770400 Free PMC article.
-
A newly designed enteral formula containing whey peptides and fermented milk product protects mice against concanavalin A-induced hepatitis by suppressing overproduction of inflammatory cytokines.Clin Nutr. 2012 Apr;31(2):283-9. doi: 10.1016/j.clnu.2011.10.012. Epub 2011 Nov 25. Clin Nutr. 2012. PMID: 22119211
-
A new immune-modulating diet enriched with whey-hydrolyzed peptide, fermented milk, and isomaltulose attenuates gut ischemia-reperfusion injury in mice.Clin Nutr. 2011 Aug;30(4):513-6. doi: 10.1016/j.clnu.2011.01.002. Epub 2011 Feb 1. Clin Nutr. 2011. PMID: 21281994
-
Acute experimental hemorrhagic-necrotizing pancreatitis induced by feeding a choline-deficient, ethionine-supplemented diet. Methodology and standards.Eur Surg Res. 1992;24 Suppl 1:40-54. doi: 10.1159/000129238. Eur Surg Res. 1992. PMID: 1601023 Review.
-
Ascites fluid in severe acute pancreatitis: from pathophysiology to therapy.Acta Gastroenterol Belg. 2000 Jul-Sep;63(3):264-8. Acta Gastroenterol Belg. 2000. PMID: 11189983 Review.
Cited by
-
Nutritional treatment with an immune-modulating enteral formula alleviates 5-fluorouracil-induced adverse effects in rats.PLoS One. 2019 Nov 26;14(11):e0225389. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0225389. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31770400 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hassoun HT, Kone BC, Mercer DW, Moody FG, Weisbrodt NW, Moore FA. 2001. Post-injury multiple organ failure: the role of the gut. Shock 15: 1–10. - PubMed
-
- Beale RJ, Bryg DJ, Bihari DJ. 1999. Immunonutrition in the critically ill: a systematic review of clinical outcome. Crit Care Med 27: 2799–2805. - PubMed
-
- Gray KD, Simovic MO, Blackwell TS, Christman JW, May AK, Parman KS, Chapman WC, Stain SC. 2006. Activation of nuclear factor kappa B and severe hepatic necrosis may mediate systemic inflammation in choline-deficient/ethionine-supplemented diet-induced pancreatitis. Pancreas 33: 260–267. - PubMed
-
- Grewal HP, Kotb M, el Din AM, Ohman M, Salem A, Gaber L, Gaber AO. 1994. Induction of tumor necrosis factor in severe acute pancreatitis and its subsequent reduction after hepatic passage. Surgery 115: 213–221. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
