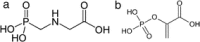Impacts of glyphosate-based herbicides on disease resistance and health of crops: a review
- PMID: 29387519
- PMCID: PMC5770481
- DOI: 10.1186/s12302-018-0131-7
Impacts of glyphosate-based herbicides on disease resistance and health of crops: a review
Abstract
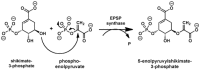
Based on experimental data from laboratory and field, numerous authors have raised concern that exposure to glyphosate-based herbicides (GBHs) may pre-dispose crops to damage by microbial pathogens. In this review, we distinguish and evaluate two principal pathways by which GBHs may affect the susceptibility of crops to disease: pathway 1-via disruptions to rhizosphere microbial ecology, and pathway 2-via restriction of nutrients to crops. We conclude that GBHs have the potential to undermine crop health in a number of ways, including: (i) impairment of the innate physiological defences of glyphosate-sensitive (GS) cultivars by interruption of the shikimic acid pathway; (ii) impairment of physiological disease defences has also been shown to occur in some glyphosate-resistant (GR) cultivars, despite their engineered resistance to glyphosate's primary mode of action; (iii) interference with rhizosphere microbial ecology (in particular, GBHs have the potential to enhance the population and/or virulence of some phytopathogenic microbial species in the crop rhizosphere); and finally, (iv) the as yet incompletely elucidated reduction in the uptake and utilisation of nutrient metals by crops. Future progress will best be achieved when growers, regulators and industry collaborate to develop products, practices and policies that minimise the use of herbicides as far as possible and maximise their effectiveness when used, while facilitating optimised food production and security.
Keywords: Glyphosate-based herbicides; Plant disease; Rhizosphere; Soil microbes.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Concerns over use of glyphosate-based herbicides and risks associated with exposures: a consensus statement.Environ Health. 2016 Feb 17;15:19. doi: 10.1186/s12940-016-0117-0. Environ Health. 2016. PMID: 26883814 Free PMC article.
-
How glyphosate affects plant disease development: it is more than enhanced susceptibility.Pest Manag Sci. 2018 May;74(5):1054-1063. doi: 10.1002/ps.4521. Epub 2017 Jan 30. Pest Manag Sci. 2018. PMID: 28067016 Review.
-
Influence of glyphosate, crop volunteer and root pathogens on glyphosate-resistant wheat under controlled environmental conditions.Pest Manag Sci. 2009 Mar;65(3):288-99. doi: 10.1002/ps.1687. Pest Manag Sci. 2009. PMID: 19115241
-
Glyphosate effects on plant mineral nutrition, crop rhizosphere microbiota, and plant disease in glyphosate-resistant crops.J Agric Food Chem. 2012 Oct 24;60(42):10375-97. doi: 10.1021/jf302436u. Epub 2012 Oct 15. J Agric Food Chem. 2012. PMID: 23013354 Free PMC article. Review.
-
History and Outlook for Glyphosate-Resistant Crops.Rev Environ Contam Toxicol. 2021;255:67-91. doi: 10.1007/398_2020_54. Rev Environ Contam Toxicol. 2021. PMID: 34109481
Cited by
-
Glyphosate residues in soil affect crop plant germination and growth.Sci Rep. 2019 Dec 23;9(1):19653. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-56195-3. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31873174 Free PMC article.
-
Lack of effects of glyphosate and glufosinate on growth, mineral content, and yield of glyphosate- and glufosinate-resistant maize.GM Crops Food. 2018;9(4):189-198. doi: 10.1080/21645698.2018.1511204. Epub 2018 Oct 16. GM Crops Food. 2018. PMID: 30325277 Free PMC article.
-
Soil Microbial Communities in Diverse Agroecosystems Exposed to the Herbicide Glyphosate.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2020 Feb 18;86(5):e01744-19. doi: 10.1128/AEM.01744-19. Print 2020 Feb 18. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 31836576 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of glyphosate and a commercial formulation Roundup® exposures on maturation of Xenopus laevis oocytes.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2020 Feb;27(4):3697-3705. doi: 10.1007/s11356-019-04596-2. Epub 2019 Mar 5. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2020. PMID: 30835066
-
The Tripartite Rhizobacteria-AM Fungal-Host Plant Relationship in Winter Wheat: Impact of Multi-Species Inoculation, Tillage Regime and Naturally Occurring Rhizobacteria Species.Plants (Basel). 2021 Jul 2;10(7):1357. doi: 10.3390/plants10071357. Plants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34371559 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Benbrook C. Impacts of genetically engineered crops on pesticide use in the US—the first sixteen years. Environmental Sciences Europe. 2012;24:24. doi: 10.1186/2190-4715-24-24. - DOI
-
- Myers JP, Antoniou MN, Blumberg B, Carroll L, Colborn T, Everett LG, Hansen M, Landrigan PJ, Lanphear BP, Mesnage R, Vandenberg LN, Vom Saal FS, Welshons WV, Benbrook CM. Concerns over use of glyphosate-based herbicides and risks associated with exposures: a consensus statement. Environ Health. 2016;15:19. doi: 10.1186/s12940-016-0117-0. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Monsanto, The agronomic benefits of glyphosate in Europe—Benefits of glyphosate per market use. Monsanto Int sàrl Monsanto Eur, 2010, 1–82
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources