Pretreatment neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio predicts worse survival outcomes and advanced tumor staging in patients undergoing radical cystectomy for bladder cancer
- PMID: 29387556
- PMCID: PMC5773045
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajur.2017.01.004
Pretreatment neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio predicts worse survival outcomes and advanced tumor staging in patients undergoing radical cystectomy for bladder cancer
Abstract
Objective: To determine the role of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) in prognosticating survival outcomes in patients with advanced/metastatic urothelial bladder cancer.
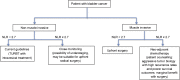
Methods: We retrospectively reviewed 84 patients undergoing radical cystectomy (RC) for UCB from January 2002 to June 2012. NLR was computed (median: 5 days) prior to surgery. No patients received neoadjuvant chemotherapy. NLR was analyzed as a continuous variable and a cut-off point of 2.7 was obtained, with a statistical receiver operating characteristics of 0.74. Kaplan-Meier curves, multivariate Cox proportional hazard and logistics regression models were used to predict NLR association with survival outcomes.
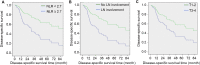
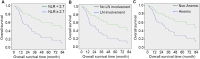
Results: The median follow-up period was 30.1 months (range: 3.2-161.7) owing to high recurrence rate and subsequent mortalities, compared to the median 64.7 months in patients alive at the end of study period. NLR ≥2.7 was associated with worse survival outcomes (5-year disease-specific survival: 22% vs 58%, p = 0.017, 95%CI: 1.193-6.009; 5-year overall survival: 23% vs 60%, p = 0.008, 95%CI: 1.322-6.147). Furthermore, on multivariate analyses, higher NLR was independently associated with higher recurrence rate (p = 0.007, HR =6.999, 95%CI: 1.712-28.606), higher T staging (p = 0.021, HR = 3.479, 95%CI: 1.212-9.990) and lymph node involvement (p = 0.009, HR = 4.534, 95%CI: 1.465-14.034).
Conclusion: This study suggests that NLR can be an inexpensive novel factor for patients risk stratification pre-operatively. This improves patient counseling and identifies patients who may benefit from multimodal treatment.
Keywords: Bladder cancer; Bladder carcinoma; Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio; Radical cystectomy.
Figures
References
-
- Stein J.P., Lieskovsky G., Cote R., Groshen S., Feng A.C., Boyd S. Radical cystectomy in the treatment of invasive bladder cancer: long-term results in 1,054 patients. J Clin Oncol. 2001;19:666–675. - PubMed
-
- Dinney C.P. Therapy of invasive bladder cancer. Urology. 2006;67:56–61. - PubMed
-
- Clark P.E., Agarwal N., Biagioli M.C., Eisenberger M.A., Greenberg R.E., Herr H.W. National comprehensive cancer N (2013) bladder cancer. J Natl Compr Cancer Netw. 2013;11:446–475. - PubMed
-
- Zehnder P., Studer U.E., Skinner E.C., Thalmann G.N., Miranda G., Roth B. Unaltered oncological outcomes of radical cystectomy with extended lymphadenectomy over three decades. BJU Int. 2013;112:E51–E58. - PubMed
-
- Malkowicz S.B., van Poppel H., Mickisch G., Pansadoro V., Thüroff J., Soloway M.S. Muscle-invasive urothelial carcinoma of the bladder. Urology. 2007;69:3–16. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources