Effects of endurance exercise and doxorubicin on skeletal muscle myogenic regulatory factor expression
- PMID: 29387634
- PMCID: PMC5774914
- DOI: 10.11138/mltj/2017.7.3.418
Effects of endurance exercise and doxorubicin on skeletal muscle myogenic regulatory factor expression
Abstract
Background: The skeletal muscle toxicity that accompanies the chemotherapy drug doxorubicin (DOX) may lead to cancer patient weakness and fatigue. This myotoxicity involves myogenic regulatory factor (MRF) disruption which alters muscle integrity and regeneration. Endurance exercise enhances MRF expression and thereby may mitigate DOX-induced MRF disruptions. This study examined the effects of endurance training and DOX treatment on myogenic regulatory factor (MRF) expression.
Methods: Male rats were exercise trained (EXER) or remained sedentary (SED) for two weeks. EXER and SED then received either DOX (15 mg/kg) or saline (SAL). Soleus, extensor digitorum longus (EDL), and diaphragm were excised 24 hours post injection, and MRF expression was analyzed.
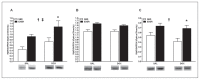
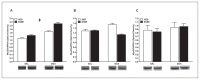
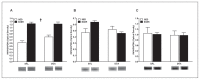
Results: Significant Myf5 drug and activity effects were observed in the soleus with EXER+DOX expressing higher Myf5 than SED+DOX. A significant drug effect was detected in soleus MyoD, and a significant activity effect was detected in soleus Mrf4. No main effects or interactions were observed in the EDL, but in the diaphragm, a significant activity effect was observed for Myf5 with EXER+DOX expressing higher levels than SED+DOX.
Conclusion: Doxorubicin treatment increased soleus MRFs and exercise boosted MRF response in soleus and diaphragm suggesting that exercise may enhance regenerative signaling with DOX treatment.
Level of evidence: I b, individual randomized controlled trial.
Keywords: anthracycline; diaphragm; fast muscle; slow muscle.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Endurance exercise training reinforces muscular strength with improvements in mitochondrial oxidative capacity, lysosome reformation, and myogenic differentiation against doxorubicin-induced skeletal muscle wasting in mice.Phys Act Nutr. 2023 Mar;27(1):76-86. doi: 10.20463/pan.2023.0010. Epub 2023 Mar 31. Phys Act Nutr. 2023. PMID: 37132214 Free PMC article.
-
Beyond Performance: Creatine Delays the Onset of Fatigue and Augments Muscle Regeneration in Doxorubicin-Induced Myotoxicity.J Med Food. 2025 Jun;28(6):625-637. doi: 10.1089/jmf.2022.0070. Epub 2025 May 23. J Med Food. 2025. PMID: 40407697
-
Resistance Training during Chemotherapy with Doxorubicin.Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2020 Dec;52(12):2529-2537. doi: 10.1249/MSS.0000000000002409. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2020. PMID: 32520871
-
Function of the myogenic regulatory factors Myf5, MyoD, Myogenin and MRF4 in skeletal muscle, satellite cells and regenerative myogenesis.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2017 Dec;72:19-32. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2017.11.011. Epub 2017 Nov 15. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2017. PMID: 29127046 Review.
-
Factors Regulating or Regulated by Myogenic Regulatory Factors in Skeletal Muscle Stem Cells.Cells. 2022 Apr 29;11(9):1493. doi: 10.3390/cells11091493. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35563799 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Restoring Skeletal Muscle Health through Exercise in Breast Cancer Patients and after Receiving Chemotherapy.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 9;25(14):7533. doi: 10.3390/ijms25147533. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39062775 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Endurance exercise training reinforces muscular strength with improvements in mitochondrial oxidative capacity, lysosome reformation, and myogenic differentiation against doxorubicin-induced skeletal muscle wasting in mice.Phys Act Nutr. 2023 Mar;27(1):76-86. doi: 10.20463/pan.2023.0010. Epub 2023 Mar 31. Phys Act Nutr. 2023. PMID: 37132214 Free PMC article.
References
-
- DeAtley SM, Aksenov MY, Aksenova MV, Harris B, Hadley R, Cole Harper P, et al. Antioxidants protect against reactive oxygen species associated with adriamycin-treated cardiomyocytes. Cancer Lett. 1999;136:41–46. - PubMed
-
- Kurabayashi M, Jeyaseelan R, Kedes L. Antineoplastic agent doxorubicin inhibits myogenic differentiation of c2 myoblasts. The Journal of biological chemistry. 1993;268:5524–5529. - PubMed
-
- Kurabayashi M, Jeyaseelan R, Kedes L. Doxorubicin represses the function of the myogenic helix-loop-helix transcription factor myod. Involvement of id gene induction. The Journal of biological chemistry. 1994;269:6031–6039. - PubMed
-
- Kobayashi J, Antoccia A, Tauchi H, Matsuura S, Komatsu K. Nbs1 and its functional role in the DNA damage response. DNA Repair (Amst) 2004;3:855–861. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
