Clinical evidence of traditional vs fast track recovery methodologies after total arthroplasty for osteoarthritic knee treatment. A retrospective observational study
- PMID: 29387645
- PMCID: PMC5774925
- DOI: 10.11138/mltj/2017.7.3.504
Clinical evidence of traditional vs fast track recovery methodologies after total arthroplasty for osteoarthritic knee treatment. A retrospective observational study
Abstract
Background: During the last years, programs to enhance postoperative recovery and decrease morbidity after total knee arthroplasty, have been developed across a variety of surgical procedures and referred to as "Fast-Track Surgery". In this study we aimed to find some answers in the management of osteoarthritic patients subjected to total knee arthroplasty, by using the Fast-Track methodology. To this purpose we evaluated parameters such as early mobilization of patients, better pain management, bleeding, possible complications, reduced hospitalization time, an overall improved recovery and patient satisfaction.
Methods: 132 patients were selected, of which, 95 treated with "Fast Track" method and 37 treated with traditional method (control group). All the patients were hospitalized and underwent the same rehabilitation program for the first three days after surgery.
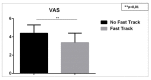
Results: In both groups, the parameters of pain and deformity demonstrated the most rapid improvement, while those of function and movement were normalized as gradual and progressive improvement over the next 2 months. The different functional test used (Barthel, MRC, VAS) showed that the mean values were significantly greater in Fast Track group when compared to the control.
Conclusion: The results of the study confirm that the application of the Fast Track protocol in orthopaedics after total knee replacement results in rapid post-surgery recovery.
Level of evidence: IV. Case series, low-quality cohort or case-control studies.
Keywords: Barthel Test; VAS score; fast track methodology; knee joint; osteoarthritis; total knee arthroplasty.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest The Authors declare that they do not have any conflict of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Musumeci G, Carnazza ML, Loreto C, Leonardi R, Loreto C. β-Defensin-4 (HBD-4) is expressed in chondrocytes derived from normal and osteoarthritic cartilage encapsulated in PEG-DA scaffold. Acta Histochem. 2012;114:805–812. - PubMed
-
- Musumeci G, Carnazza ML, Leonardi R, Loreto C. Expression of β-defensin-4 in “an in vivo and ex vivo model” of human osteoarthritic knee meniscus. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2012;20:216–222. - PubMed
-
- Musumeci G, Loreto C, Clementi G, Fiore CE, Martinez G. An in vivo experimental study on osteopenia in diabetic rats. Acta Histochem. 2011;113:619–625. - PubMed
-
- Musumeci G, Szychlinska MA, Mobasheri A. Age-related degeneration of articular cartilage in the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis: molecular markers of senescent chondrocytes. Histol Histopathol. 2015;30:1–12. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
