Beneficial Effects of Selective Orexin-A Receptor Antagonist in 4-aminopyridine-induced Seizures in Male Rats
- PMID: 29387673
- PMCID: PMC5767796
- DOI: 10.4103/abr.abr_262_16
Beneficial Effects of Selective Orexin-A Receptor Antagonist in 4-aminopyridine-induced Seizures in Male Rats
Abstract
Background: Orexins are excitatory neuropeptides which stimulate the central regulatory pathways. Orexins increase the penicillin-induced epileptic activity in rats. Orexin-A increases in different types of seizures and its elevated level is the characteristic feature in the epileptic children during polysomnography. Recently, the orexin receptor blockage has been reported to increase seizure threshold in mice; however, effect of the selective orexin-A receptor antagonist (SB-334867) on 4-aminopyridine (4-AP)-induced seizures has not been investigated.
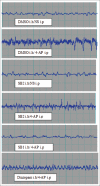
Materials and methods: We used the intraperitoneal injection of 4-AP to induce seizure in male rats. Under urethane anesthesia, SB-334867 (50 and 100 nmol) was injected stereotaxically into the ventral hippocampal commissure. Using video recording, the effects of SB-334867 on electroencephalogram and tonic-clonic convulsions were compared to those that received diazepam or dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO).
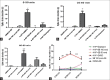
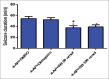
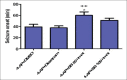
Results: SB-334867 significantly decreased the duration of spike trains compared to DMSO-treated rats (P < 0.001) and reduced the duration of convulsive seizures (P < 0.05). Seizure onset was increased significantly by SB-334867, 50 nmol, compared to DMSO (P < 0.05) and diazepam (P < 0.01) treated rats.
Conclusion: Antagonism of orexin-A receptor by a low-dose SB-334867 showed protective effects in 4-AP-induced seizure-like activities in anesthetized rats.
Keywords: 4-aminopyridine; electroencephalogram; microinjection; orexin-A receptor antagonist.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
SB 334867, a selective orexin receptor type 1 antagonist, elevates seizure threshold in mice.Life Sci. 2016 Apr 1;150:81-8. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2016.02.075. Epub 2016 Feb 23. Life Sci. 2016. PMID: 26916826
-
Hippocampal orexin receptors inactivation reduces PTZ induced seizures of male rats.Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2015 Mar;130:77-83. doi: 10.1016/j.pbb.2015.01.006. Epub 2015 Jan 17. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2015. PMID: 25600753
-
SB-334867, an orexin receptor 1 antagonist, decreased seizure and anxiety in pentylenetetrazol-kindled rats.Fundam Clin Pharmacol. 2017 Apr;31(2):201-207. doi: 10.1111/fcp.12249. Epub 2016 Nov 23. Fundam Clin Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 27739093
-
Menthol Dissolved in Dimethyl Sulfoxide Protects Against Epileptiform Activity Induced by Pentylenetetrazol in Male Rats.Basic Clin Neurosci. 2023 Nov-Dec;14(6):805-812. doi: 10.32598/bcn.2022.3025.1. Epub 2023 Nov 1. Basic Clin Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 39070199 Free PMC article.
-
Orexins and appetite regulation.Neuropeptides. 2002 Oct;36(5):303-25. doi: 10.1016/s0143-4179(02)00085-9. Neuropeptides. 2002. PMID: 12450737 Review.
Cited by
-
Can serum orexin levels be used as a marker in childhood epilepsy?Heliyon. 2024 Dec 14;11(1):e41145. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e41145. eCollection 2025 Jan 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39811283 Free PMC article.
-
Intranigral Administration of β-Sitosterol-β-D-Glucoside Elicits Neurotoxic A1 Astrocyte Reactivity and Chronic Neuroinflammation in the Rat Substantia Nigra.J Immunol Res. 2020 Nov 16;2020:5907591. doi: 10.1155/2020/5907591. eCollection 2020. J Immunol Res. 2020. PMID: 33282962 Free PMC article.
-
Suvorexant, a Dual Orexin Receptor Antagonist, Protected Seizure through Interaction with GABAA and Glutamate Receptors.Iran J Pharm Res. 2020 Spring;19(2):383-390. doi: 10.22037/ijpr.2019.14688.12584. Iran J Pharm Res. 2020. PMID: 33224245 Free PMC article.
-
Sleep fragmentation and decreased REM sleep in a primate model of diurnal cortical seizures.Epilepsy Res. 2021 Dec;178:106805. doi: 10.1016/j.eplepsyres.2021.106805. Epub 2021 Nov 2. Epilepsy Res. 2021. PMID: 34768048 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tsujino N, Sakurai T. Orexin/hypocretin: A neuropeptide at the interface of sleep, energy homeostasis, and reward system. Pharmacol Rev. 2009;61:162–76. - PubMed
-
- Kilduff TS, Peyron C. The hypocretin/orexin ligand-receptor system: Implications for sleep and sleep disorders. Trends Neurosci. 2000;23:359–65. - PubMed
-
- Samson WK, Bagley SL, Ferguson AV, White MM. Hypocretin/orexin type 1 receptor in brain: Role in cardiovascular control and the neuroendocrine response to immobilization stress. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2007;292:R382–7. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

