Neutrophil Extracellular Traps Are Pathogenic in Ventilator-Induced Lung Injury and Partially Dependent on TLR4
- PMID: 29387725
- PMCID: PMC5745654
- DOI: 10.1155/2017/8272504
Neutrophil Extracellular Traps Are Pathogenic in Ventilator-Induced Lung Injury and Partially Dependent on TLR4
Abstract
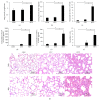
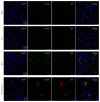
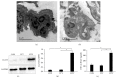
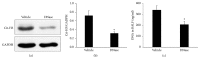
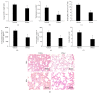
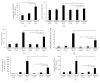
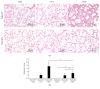
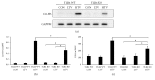
The pathogenesis of ventilator-induced lung injury (VILI) is associated with neutrophils. Neutrophils release neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs), which are composed of DNA and granular proteins. However, the role of NETs in VILI remains incompletely understood. Normal saline and deoxyribonuclease (DNase) were used to study the role of NETs in VILI. To further determine the role of Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) in NETosis, we evaluated the lung injury and NET formation in TLR4 knockout mice and wild-type mice that were mechanically ventilated. Some measures of lung injury and the NETs markers were significantly increased in the VILI group. DNase treatment markedly reduced NETs markers and lung injury. After high-tidal mechanical ventilation, the NETs markers in the TLR4 KO mice were significantly lower than in the WT mice. These data suggest that NETs are generated in VILI and pathogenic in a mouse model of VILI, and their formation is partially dependent on TLR4.
Figures
References
-
- Imai Y., Kawano T., Miyasaka K., Takata M., Imai T., Okuyama K. Inflammatory chemical mediators during conventional ventilation and during high frequency oscillatory ventilation. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine. 1994;150(6 I):1550–1554. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm.150.6.7952613. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Imanaka H., Shimaoka M., Matsuura N., Nishimura M., Ohta N., Kiyono H. Ventilator-induced lung injury is associated with neutrophil infiltration, macrophage activation, and TGF-β1 mRNA upregulation in rat lungs. Anesthesia & Analgesia. 2001;92(2):428–436. doi: 10.1213/00000539-200102000-00029. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

