Beneficial effects of thyroid hormone on adipose inflammation and insulin sensitivity of obese Wistar rats
- PMID: 29388360
- PMCID: PMC5817825
- DOI: 10.14814/phy2.13550
Beneficial effects of thyroid hormone on adipose inflammation and insulin sensitivity of obese Wistar rats
Abstract
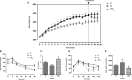
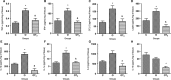
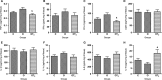
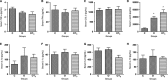
Thyroid hormones play an important role in glucose metabolism and there is evidence of increased prevalence of thyroid dysfunction in obese and diabetic patients. This study aimed at evaluating the thyroid function and the effects of the triiodothyronine (T3) treatment on glycemia control, insulin sensitivity and subclinical inflammation in cafeteria-diet-induced obesity in rats. Obesity was induced in male Wistar rats by offering a cafeteria diet and a subset of the obese rats was treated with T3 (1.5 μg per 100 g of body weight) for a 28-day period. The pituitary-thyroid axis was evaluated by molecular and biochemical parameters. Cytokine content was measured in the serum as well as in the mesenteric and epididymal white adipose tissue. Obese rats exhibited impairment of glycemia control, increased content of inflammatory cytokines in mesenteric white adipose tissue, decreased serum thyrotropin (TSH) concentration and increased sodium/iodide symporter (NIS) and TSH receptor (TSHR) protein content in thyroid gland. T3 treatment improved insulin sensitivity, glucose tolerance, and reduced inflammatory cytokine content in mesenteric white adipose tissue. In the thyroid gland NIS, TSHR, and thyroperoxidase (TPO) content were reduced while thyroglobulin (TG) content was increased by T3. The thyrotrophic response to negative feedback exerted by T3 was preserved in obese rats. The present data reinforce the beneficial effects of T3 treatment of obese rats on the improvement of insulin sensitivity and on the negative modulation of inflammatory cytokine expression in adipose tissue. Moreover, we have evidenced that the pituitary-thyroid axis is affected in obese rats, as illustrated by the impaired TSH secretion.
Keywords: Adipose tissue; cytokines; insulin sensitivity; obesity; triiodothyronine.
© 2018 The Authors. Physiological Reports published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. on behalf of The Physiological Society and the American Physiological Society.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Thyroid hormone reduces inflammatory cytokines improving glycaemia control in alloxan-induced diabetic wistar rats.Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2016 Jun;217(2):130-40. doi: 10.1111/apha.12647. Epub 2016 Jan 30. Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2016. PMID: 26748816
-
Moderate doses of iodide in vivo inhibit cell proliferation and the expression of thyroperoxidase and Na+/I- symporter mRNAs in dog thyroid.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1997 Aug 8;131(2):195-203. doi: 10.1016/s0303-7207(97)00108-1. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1997. PMID: 9296378
-
Therapeutical Potential of T3 as Adjuvant Therapy in Male Alloxan-induced Diabetic Rats.Endocrinology. 2024 May 27;165(7):bqae066. doi: 10.1210/endocr/bqae066. Endocrinology. 2024. PMID: 38862394
-
Thyroglobulin regulates follicular function and heterogeneity by suppressing thyroid-specific gene expression.Biochimie. 1999 Apr;81(4):329-40. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(99)80078-9. Biochimie. 1999. PMID: 10401666 Review.
-
Glycosylation in the Thyroid Gland: Vital Aspects of Glycoprotein Function in Thyrocyte Physiology and Thyroid Disorders.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Sep 17;19(9):2792. doi: 10.3390/ijms19092792. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30227620 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Circulating metabolite profile in young adulthood identifies long-term diabetes susceptibility: the Coronary Artery Risk Development in Young Adults (CARDIA) study.Diabetologia. 2022 Apr;65(4):657-674. doi: 10.1007/s00125-021-05641-x. Epub 2022 Jan 18. Diabetologia. 2022. PMID: 35041022 Free PMC article.
-
Maternal hypothyroidism in mice influences glucose metabolism in adult offspring.Diabetologia. 2020 Sep;63(9):1822-1835. doi: 10.1007/s00125-020-05172-x. Epub 2020 May 30. Diabetologia. 2020. PMID: 32472193 Free PMC article.
-
Spermatogonial Type 3 Deiodinase Regulates Thyroid Hormone Target Genes in Developing Testicular Somatic Cells.Endocrinology. 2019 Dec 1;160(12):2929-2945. doi: 10.1210/en.2019-00259. Endocrinology. 2019. PMID: 31621880 Free PMC article.
-
Adipose Tissue Remodeling in Obesity: An Overview of the Actions of Thyroid Hormones and Their Derivatives.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023 Apr 10;16(4):572. doi: 10.3390/ph16040572. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37111329 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interplay between Fatty Acid Binding Protein 4, Fetuin-A, Retinol Binding Protein 4 and Thyroid Function in Metabolic Dysregulation.Metabolites. 2022 Mar 29;12(4):300. doi: 10.3390/metabo12040300. Metabolites. 2022. PMID: 35448487 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bargi‐Souza, P. , Romano R. M., Salgado Rde M., Goulart‐Silva F., Brunetto E. L., Zorn T. M., et al. 2013. Triiodothyronine rapidly alters the TSH content and the secretory granules distribution in male rat thyrotrophs by a cytoskeleton rearrangement‐independent mechanism. Endocrinol. 154:4908–4918. - PubMed
-
- Bargi‐Souza, P. , Goulart‐Silva F., and Nunes M. T.. 2017. Novel aspects of T3 actions on GH and TSH synthesis and secretion: physiological implications. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 59:R167–R178. https://doi.org/10.1530/jme-17-0068. [Epub ahead of print] - DOI - PubMed
-
- Biscolla, R. P. M. , Chiamolera M. I., Kanashiro I., Maciel R. M. B., and Vieira J. G. H.. 2017. A Single 10 mg Oral Dose of Biotin Interferes with Thyroid Function Tests. Thyroid 27:1099–1100. - PubMed
-
- Borges, P. P. , Curty F. H., Pazos‐Moura C. C., and Moura E. G.. 1998. Effect of testosterone propionate treatment on thyrotropin secretion of young and old rats in vitro . Life Sci. 62:2035–2043. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

