Multi-compartmental diffusion characterization of the human cervical spinal cord in vivo using the spherical mean technique
- PMID: 29388719
- PMCID: PMC5854548
- DOI: 10.1002/nbm.3894
Multi-compartmental diffusion characterization of the human cervical spinal cord in vivo using the spherical mean technique
Abstract
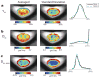
The purpose of this work was to evaluate the feasibility and reproducibility of the spherical mean technique (SMT), a multi-compartmental diffusion model, in the spinal cord of healthy controls, and to assess its ability to improve spinal cord characterization in multiple sclerosis (MS) patients at 3 T. SMT was applied in the cervical spinal cord of eight controls and six relapsing-remitting MS patients. SMT provides an elegant framework to model the apparent axonal volume fraction vax , intrinsic diffusivity Dax , and extra-axonal transverse diffusivity Dex_perp (which is estimated as a function of vax and Dax ) without confounds related to complex fiber orientation distribution that reside in diffusion MRI modeling. SMT's reproducibility was assessed with two different scans within a month, and SMT-derived indices in healthy and MS cohorts were compared. The influence of acquisition scheme on SMT was also evaluated. SMT's vax , Dax , and Dex_perp measurements all showed high reproducibility. A decrease in vax was observed at the site of lesions and normal appearing white matter (p < 0.05), and trends towards a decreased Dax and increased Dex_perp were seen. Importantly, a twofold reduction in acquisition yielded similarly high accuracy with SMT. SMT provides a fast, reproducible, and accurate method to improve characterization of the cervical spinal cord, and may have clinical potential for MS patients.
Keywords: axon; diffusion; multiple sclerosis; spherical mean technique; spinal cord; volume fraction.
Copyright © 2018 John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
Figures



References
-
- Le Bihan D, Breton E, Lallemand D, Grenier P, Cabanis E, Laval-Jeantet M. MR imaging of intravoxel incoherent motions: application to diffusion and perfusion in neurologic disorders. Radiology. 1986;161(2):401–407. - PubMed
-
- Song SK, Yoshino J, Le TQ, et al. Demyelination increases radial diffusivity in corpus callosum of mouse brain. NeuroImage. 2005;26(1):132–140. - PubMed
-
- Niendorf T, Dijkhuizen RM, Norris DG, van Lookeren Campagne M, Nicolay K. Biexponential diffusion attenuation in various states of brain tissue: Implications for diffusion - weighted imaging. Magn Reson Med. 1996;36(6):847–857. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

