Special AT-rich sequence binding protein 1 is required for maintenance of T cell receptor responsiveness and development of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis
- PMID: 29388727
- PMCID: PMC5947310
- DOI: 10.1111/1348-0421.12579
Special AT-rich sequence binding protein 1 is required for maintenance of T cell receptor responsiveness and development of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis
Abstract
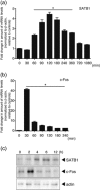
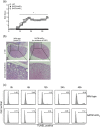
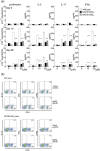
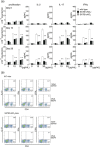
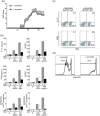
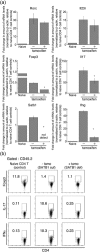
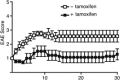
The genome organizer special AT-rich sequence binding protein 1 (SATB1) regulates specific functions through chromatin remodeling in T helper cells. It was recently reported by our team that T cells from SATB1 conditional knockout (SATB1cKO) mice, in which the Satb1 gene is deleted from hematopoietic cells, impair phosphorylation of signaling molecules in response to T cell receptor (TCR) crosslinking. However, in vivo T cell responses upon antigen presentation in the absence of SATB1 remain unclear. In the current study, it was shown that SATB1 modulates T cell antigen responses during the induction and effector phases. Expression of SATB1 was upregulated in response to TCR stimulation, suggesting that SATB1 is important for this antigen response. The role of SATB1 in TCR responses and induced experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) was therefore examined using the myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein peptide 35-55 (MOG35-55) and pertussis toxin. SATB1cKO mice were found to be resistant to EAE and had defects in IL-17- and IFN-γ-producing pathogenic T cells. Thus, SATB1 expression appears necessary for T cell function in the induction phase. To examine SATB1 function during the effector phase, a tamoxifen-inducible SATB1 deletion system, SATB1cKO-ER-Cre mice, was used. Encephalitogenic T cells from MOG35-55-immunized SATB1cKO-ER-Cre mice were transferred into healthy mice. Mice that received tamoxifen before the onset of paralysis were resistant to EAE. Furthermore, no disease progression occurred in recipient mice treated with tamoxifen after the onset of EAE. Thus, SATB1 is essential for maintaining TCR responsiveness during the induction and effector phases and may provide a novel therapeutic target for T cell-mediated autoimmune diseases.
Keywords: T cell receptor response; autoimmune disease; experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis model; special AT-rich sequence binding protein 1.
© 2018 The Authors. Microbiology and Immunology Published by The Societies and John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd.
Figures

References
-
- Schneider R., Grosschedl R (2007) Dynamics and interplay of nuclear architecture, genome organization, and gene expression. Genes Dev 21: 3027–43. - PubMed
-
- Cockerill P.N., Yuen M.H., Garrard W.T. (1987) The enhancer of the immunoglobulin heavy chain locus is flanked by presumptive chromosomal loop anchorage elements. J Biol Chem 262: 5394–97. - PubMed
-
- Zlatanova J.S., van Holde K.E. (1992) Chromatin loops and transcriptional regulation. Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Exp 2: 211–24. - PubMed
-
- Banan M., Rojas I.C., Lee W.H., King H.L., Harriss J.V., Kobayashi R, Webb C.F., Gottlieb P.D. (1997) Interaction of the nuclear matrix‐associated region (MAR)‐binding proteins, SATB1 and CDP/Cux, with a MAR element (L2a) in an upstream regulatory region of the mouse CD8a gene. J Biol Chem 272: 18440–52. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

