The Road from Host-Defense Peptides to a New Generation of Antimicrobial Drugs
- PMID: 29389911
- PMCID: PMC6017364
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules23020311
The Road from Host-Defense Peptides to a New Generation of Antimicrobial Drugs
Abstract
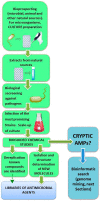
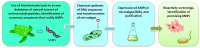
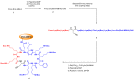
Host-defense peptides, also called antimicrobial peptides (AMPs), whose protective action has been used by animals for millions of years, fulfill many requirements of the pharmaceutical industry, such as: (1) broad spectrum of activity; (2) unlike classic antibiotics, they induce very little resistance; (3) they act synergically with conventional antibiotics; (4) they neutralize endotoxins and are active in animal models. However, it is considered that many natural peptides are not suitable for drug development due to stability and biodisponibility problems, or high production costs. This review describes the efforts to overcome these problems and develop new antimicrobial drugs from these peptides or inspired by them. The discovery process of natural AMPs is discussed, as well as the development of synthetic analogs with improved pharmacological properties. The production of these compounds at acceptable costs, using different chemical and biotechnological methods, is also commented. Once these challenges are overcome, a new generation of versatile, potent and long-lasting antimicrobial drugs is expected.
Keywords: AMP; antibiotic; antimicrobial; cathelicidins; customizable units; gene mining; peptide modification; peptides; site-selective; tag-and-modify.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


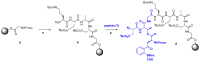

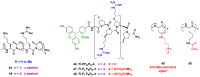
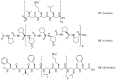
References
-
- Wang G., editor. Antimicrobial Peptides: Discovery, Design and Novel Therapeutic Strategies. 2nd ed. Centre for Agriculture and Bioscience International (CABI); Wallingford, UK: 2017. ISBN 978-1-786390394 (hardback), 978-1-786390400 (e-book)
-
- Kastin A.J., editor. Handbook of Biologically Active Peptides. Academic Press; San Diego, CA, USA: 2006.
-
- For Antimicrobial Peptide Databases. Antimicrobial Peptide Database-APD. [(accessed on 16 January 2018)]; Available online: http://aps.unmc.edu/AP/main.php.
-
- Data Repository of Antimicrobial Peptides-DRAMP. [(accessed on 16 January 2018)]; Available online: http://dramp.cpu-bioinfor.org/
-
- Defensins Knowledgebase. [(accessed on 16 January 2018)]; Available online: http://defensins.bii.a-star.edu.sg/
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

