Strengths use as a secret of happiness: Another dimension of visually impaired individuals' psychological state
- PMID: 29389991
- PMCID: PMC5794170
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0192323
Strengths use as a secret of happiness: Another dimension of visually impaired individuals' psychological state
Abstract
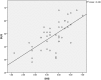
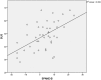
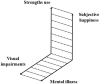
It is well recognized that visual impairments (VI) worsen individuals' mental condition. However, little is known about the positive aspects including subjective happiness, positive emotions, and strengths. Therefore, the purpose of this study was to investigate the positive aspects of persons with VI including their subjective happiness, positive emotions, and strengths use. Positive aspects of persons with VI were measured using the Subjective Happiness Scale (SHS), the Scale of Positive and Negative Experience-Balance (SPANE-B), and the Strengths Use Scale (SUS). A cross-sectional analysis was utilized to examine personal information in a Tokyo sample (N = 44). We used a simple regression analysis and found significant relationships between the SHS or SPANE-B and SUS; on the contrary, VI-related variables were not correlated with them. A multiple regression analysis confirmed that SUS was a significant factor associated with both the SHS and SPANE-B. Strengths use might be a possible protective factor from the negative effects of VI.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Measuring the frequency of emotions-validation of the Scale of Positive and Negative Experience (SPANE) in Germany.PLoS One. 2017 Feb 8;12(2):e0171288. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0171288. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28178328 Free PMC article.
-
[Subjective happiness among Japanese adults: An upward tendency associated with age].Nihon Koshu Eisei Zasshi. 2018;65(9):553-562. doi: 10.11236/jph.65.9_553. Nihon Koshu Eisei Zasshi. 2018. PMID: 30587678 Japanese.
-
Wellbeing perception of institutional caregivers working for people with disabilities: use of Subjective Happiness Scale and Satisfaction with Life Scale analyses.Res Dev Disabil. 2010 Sep-Oct;31(5):1083-90. doi: 10.1016/j.ridd.2010.03.009. Epub 2010 Apr 18. Res Dev Disabil. 2010. PMID: 20400262
-
Extent of Exacerbation of Chronic Health Conditions by Visual Impairment in Terms of Health-Related Quality of Life.JAMA Ophthalmol. 2015 Nov;133(11):1267-75. doi: 10.1001/jamaophthalmol.2015.3055. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2015. PMID: 26379209
-
Impact of severity and bilaterality of visual impairment on health-related quality of life.Ophthalmology. 2006 Oct;113(10):1846-53. doi: 10.1016/j.ophtha.2006.04.028. Epub 2006 Aug 4. Ophthalmology. 2006. PMID: 16889831
Cited by
-
Value of considering psychological strengths in patients with eye pain.Am J Ophthalmol Case Rep. 2018 Oct 11;12:91-92. doi: 10.1016/j.ajoc.2018.10.003. eCollection 2018 Dec. Am J Ophthalmol Case Rep. 2018. PMID: 30364663 Free PMC article.
-
Changes in patient subjective happiness and satisfaction with cataract surgery.Sci Rep. 2020 Oct 14;10(1):17273. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-72846-2. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 33057036 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mangione CM, Gutierrez PR, Lowe G, Orav EJ, Seddon JM. Influence of age-related maculopathy on visual functioning and health-related quality of life. Am J Ophthalmol 1999; 128(1): 45–53. - PubMed
-
- Broman AT, Munoz B, Rodriguez J, Sanchez R, Quigley HA, Klein R, et al. The impact of visual impairment and eye disease on vision-related quality of life in a Mexican-American population: proyecto VER. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2002; 43(11): 3393–3398. - PubMed
-
- Swanson MW, McGwin G. Visual impairment and functional status from the 1995 National Health Interview Survey on Disability. Ophthalmic Epidemiol 2004; 11(3): 227–239. doi: 10.1080/09286580490514540 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Steinberg EP, Tielsch JM, Schein OD, Javitt JC, Sharkey P, Cassard SD, et al. The VF-14. An index of functional impairment in patients with cataract. Arch Ophthalmol 1994; 112(5): 630–638. - PubMed
-
- Papadopoulos K, Montgomery AJ, Chronopoulou E. The impact of visual impairments in self-esteem and locus of control. Res Dev Disabil 2013; 34(12): 4565–4570. doi: 10.1016/j.ridd.2013.09.036 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

