The Arabidopsis COPII components, AtSEC23A and AtSEC23D, are essential for pollen wall development and exine patterning
- PMID: 29390074
- PMCID: PMC5889017
- DOI: 10.1093/jxb/ery015
The Arabidopsis COPII components, AtSEC23A and AtSEC23D, are essential for pollen wall development and exine patterning
Abstract
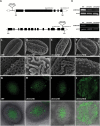
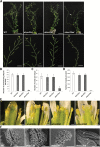
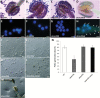
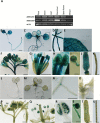
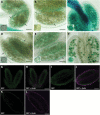
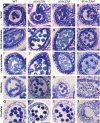
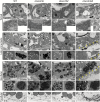
The specialized multilayered pollen wall plays multiple roles to ensure normal microspore development. The major components of the pollen wall (e.g. sporopollenin and lipidic precursors) are provided from the tapetum. Material export from the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is mediated by coat protein complex II (COPII) vesicles. The Arabidopsis thaliana genome encodes seven homologs of SEC23, a COPII component. However, the functional importance of this diversity remains elusive. Here, we analyzed knockout and knockdown lines for AtSEC23A and AtSEC23D, two of the A. thaliana SEC23 homologs, respectively. Single atsec23a and atsec23d mutant plants, despite normal fertility, showed an impaired exine pattern. Double atsec23ad mutant plants were semi-sterile and exhibited developmental defects in pollen and tapetal cells. Pollen grains of atsec23ad had defective exine and intine, and showed signs of cell degeneration. Moreover, the development of tapetal cells was altered, with structural abnormalities in organelles. AtSEC23A and AtSEC23D exhibited the characteristic localization pattern of COPII proteins and were highly expressed in the tapetum. Our work suggests that AtSEC23A and AtSEC23D may organize pollen wall development and exine patterning by regulating ER export of lipids and proteins necessary for pollen wall formation. Also, our results shed light on the functional heterogeneity of SEC23 homologs.
Figures


References
-
- Aarts MG, Hodge R, Kalantidis K, Florack D, Wilson ZA, Mulligan BJ, Stiekema WJ, Scott R, Pereira A. 1997. The Arabidopsis MALE STERILITY 2 protein shares similarity with reductases in elongation/condensation complexes. The Plant Journal 12, 615–623. - PubMed
-
- Aboulela M, Tanaka Y, Nishimura K, Mano S, Nishimura M, Ishiguro S, Kimura T, Nakagawa T. 2017. Development of an R4 dual-site (R4DS) gateway cloning system enabling the efficient simultaneous cloning of two desired sets of promoters and open reading frames in a binary vector for plant research. PLoS One 12, e0177889. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Alexander MP. 1969. Differential staining of aborted and nonaborted pollen. Stain Technology 44, 117–122. - PubMed
-
- Alonso JM, Stepanova AN, Leisse TJ et al. 2003. Genome-wide insertional mutagenesis of Arabidopsis thaliana. Science 301, 653–657. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

