NT-proBNP test with improved accuracy for the diagnosis of chronic heart failure
- PMID: 29390456
- PMCID: PMC5758158
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000009181
NT-proBNP test with improved accuracy for the diagnosis of chronic heart failure
Abstract
The circulating concentration of N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) has been shown to be a diagnostic tool for the detection of heart failure. Several factors influence NT-proBNP levels including age, sex, and body mass index (BMI). Therefore, the diagnostic sensitivity of NT-proBNP level for heart failure is relatively higher, but its specificity is low. This study aims to improve the diagnostic accuracy rate of this test by including multiple variables in the diagnostic test.The suspected chronic heart failure outpatients were divided into heart failure with reduced ejection fraction, heart failure with mid-range ejection fraction, heart failure with preserved ejection fraction, and normal heart function groups. Area under the receiver-operating characteristic (ROC) curve, cut-off value, and logistic regression analysis were used to select the model variables, sensitivity and specificity.In all, 436 subjects enrolled into this study were divided in 2 groups: model establishment (n = 300) and model validation (n = 136). In the model establishment group, the area under the curve (AUC) and cut-off value of NT-proBNP was 0.926 and 257.4 pg/mL, respectively. When age, glomerular filtration rate, BMI, atrial fibrillation, and sex were entered into the diagnosis model, AUC, sensitivity, and specificity further increased to 0.955 (95% confidence interval [CI] 0.934, 0.976), 94.2% (from 93.0%), and 86.7% (from 74.2%). The ROC curve of corrected NT-proBNP diagnostic formula for heart failure was also significantly higher (P = .037).The corrected NT-proBNP diagnostic formula was found to improve the diagnostic accuracy of chronic heart failure.
Copyright © 2017 The Authors. Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared that they had no conflicts of interest.
Figures
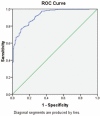

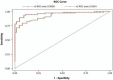
References
-
- Daniels LB, Maisel AS. Natriuretic peptides. J Am Coll Cardiol 2007;50:2357–68. - PubMed
-
- Hall C. Essential biochemistry and physiology of (NT-pro)BNP. Eur J Heart Fail 2004;6:257–60. - PubMed
-
- Maisel AS, Krishnaswamy P, Nowak RM, et al. Rapid measurement of B-type natriuretic peptide in the emergency diagnosis of heart failure. N Engl J Med 2002;347:161–7. - PubMed
-
- Januzzi JL, Jr, Camargo CA, Anwaruddin S, et al. The N-terminal Pro-BNP investigation of dyspnea in the emergency department (PRIDE) study. Am J Cardiol 2005;95:948–54. - PubMed
-
- Maisel A, Hollander JE, Guss D, et al. Primary results of the Rapid Emergency Department Heart Failure Outpatient Trial (REDHOT). A multicenter study of B-type natriuretic peptide levels, emergency department decision making, and outcomes in patients presenting with shortness of breath. J Am Coll Cardiol 2004;44:1328–33. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

