PHLPP1 mediates melanoma metastasis suppression through repressing AKT2 activation
- PMID: 29391600
- PMCID: PMC6450546
- DOI: 10.1038/s41388-017-0061-7
PHLPP1 mediates melanoma metastasis suppression through repressing AKT2 activation
Abstract
PI3K/AKT pathway activation is thought to be a driving force in metastatic melanomas. Members of the pleckstrin homology (PH) domain leucine-rich repeat protein Ser/Thr specific phosphatase family (PHLPP1 and PHLPP2) can regulate AKT activation. By dephosphorylating specific serine residues in the hydrophobic motif, PHLPP1 and PHLPP2 restrain AKT signalings, thereby regulating cell proliferation and survival. We here show that PHLPP1 expression was significantly downregulated or lost and correlated with metastatic potential in melanoma. Forcing expression of either PHLPP1 or PHLPP2 in melanoma cells inhibited cell proliferation, migration, and colony formation in soft agar; but PHLPP1 had the most profound inhibitory effect on metastasis. Moreover, expression of PH mutant forms of PHLPP1 continued to inhibit metastasis, whereas a phosphatase-dead C-terminal mutant did not. The introduction of activated PHLPP1-specific targets AKT2 or AKT3 also promoted melanoma metastasis, while the non-PHLPP1 target AKT1 did not. AKT2 and AKT3 could even rescue the PHLPP1-mediated inhibition of metastasis. An AKT inhibitor blocked the activity of AKT2 and inhibited AKT2-mediated tumor growth and metastasis in a preclinical mouse model. Our data demonstrate that PHLPP1 functions as a metastasis suppressor through its phosphatase activity, and suggest that PHLPP1 represents a novel diagnostic and therapeutic marker for metastatic melanoma.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Figures
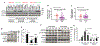
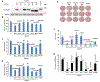
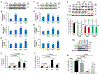
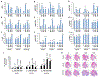

References
-
- Alonso A, Sasin J, Bottini N, Friedberg I, Friedberg I, Osterman A et al. Protein tyrosine phosphatases in the human genome. Cell 2004; 117(6):699–711. - PubMed
-
- Julien SG, Dubé N, Hardy S, Tremblay ML. Inside the human cancer tyrosine phosphatome. Nat Rev Cancer 2011; 11(1):35–49. - PubMed
-
- Blume-Jensen P, Hunter T. Oncogenic kinase signaling. Nature 2001; 411(6835):355–365. - PubMed
-
- Ostman A, Hellberg C, Böhmer FD. Protein-tyrosine phosphatases and cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 2006; 6(4):307–320. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

