Cellular Therapeutics for Heart Failure: Focus on Mesenchymal Stem Cells
- PMID: 29391871
- PMCID: PMC5748110
- DOI: 10.1155/2017/9640108
Cellular Therapeutics for Heart Failure: Focus on Mesenchymal Stem Cells
Abstract
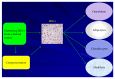
Resulting from a various etiologies, the most notable remains ischemia; heart failure (HF) manifests as the common end pathway of many cardiovascular processes and remains among the top causes for hospitalization and a major cause of morbidity and mortality worldwide. Current pharmacologic treatment for HF utilizes pharmacologic agents to control symptoms and slow further deterioration; however, on a cellular level, in a patient with progressive disease, fibrosis and cardiac remodeling can continue leading to end-stage heart failure. Cellular therapeutics have risen as the new hope for an improvement in the treatment of HF. Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) have gained popularity given their propensity of promoting endogenous cellular repair of a myriad of disease processes via paracrine signaling through expression of various cytokines, chemokines, and adhesion molecules resulting in activation of signal transduction pathways. While the exact mechanism remains to be completely elucidated, this remains the primary mechanism identified to date. Recently, MSCs have been incorporated as the central focus in clinical trials investigating the role how MSCs can play in the treatment of HF. In this review, we focus on the characteristics of MSCs that give them a distinct edge as cellular therapeutics and present results of clinical trials investigating MSCs in the setting of ischemic HF.
Figures
References
-
- Pandey A. C., Semon J. A., Kaushal D., et al. MicroRNA profiling reveals age-dependent differential expression of nuclear factor κB and mitogen-activated protein kinase in adipose and bone marrow-derived human mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cell Research & Therapy. 2011;2(6):p. 49. doi: 10.1186/scrt90. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ortiz L. A., Dutreil M., Fattman C., et al. Interleukin 1 receptor antagonist mediates the antiinflammatory and antifibrotic effect of mesenchymal stem cells during lung injury. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2007;104(26):11002–11007. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0704421104. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

