Recurrent Pleomorphic Adenoma of the Submandibular Gland
- PMID: 29392015
- PMCID: PMC5782975
- DOI: 10.5152/tao.2016.1281
Recurrent Pleomorphic Adenoma of the Submandibular Gland
Abstract
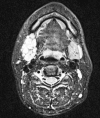
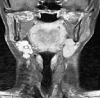
Pleomorphic adenoma (PA) is the most common benign tumor of salivary glands. Most PAs occur in the parotid (80%), followed by the submandibular gland (10%) and minor salivary and sublingual glands (10%). Submandibular gland PAs usually manifest in the submandibular area as a painless hard mass. Although several recurrent parotid gland PA cases have been reported in the literature, recurrent submandibular gland PA is quite rare. Complete surgical removal of tumor of the submandibular gland and keeping the capsule intact are important to prevent recurrence. Here we present a rare case of submandibular gland PA recurrence that occurred 5 years after the first surgery and methods to prevent recurrence.
Keywords: Submandibular gland; pleomorphic adenoma; surgery.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: No conflict of interest was declared by the authors.
Figures


References
-
- Spiro RH. Salivary neoplasms: overview of a 35-year experience with 2807 patients. Head Neck Surg. 1986;8:177–84. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/hed.2890080309. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Seifert G, Miehlke A, Haubrich J, Chilla R. Diseases of the salivary glands. New York: Thieme; 1986. p. 408.
-
- Donovan DT, Conley JJ. Capsular significance in parotid tumorsurgery: reality and myths of lateral lobectomy. Laryngoscope. 1984;94:324–32. - PubMed
-
- Soares AB, Altemani A, de Araújo VC. Study of histopathological, morphological and immunohistochemical features of recurrent pleomorphic adenoma: an attempt to predict recurrence of pleomorphic adenoma. J Oral Pathol Med. 2011;40:352–8. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0714.2010.00956.x. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Henriksson G, Westrin KM, Carlsoo B, Silfversward C. Recurrent primary pleomorphic adenomas of salivary gland origin: intrasurgical rupture, histopathologic features, and pseudopodia. Cancer. 1998;82:617–20. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1097-0142(19980215)82:4<617::AID-CNCR1>3.... - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
