Immune modulatory effects of statins
- PMID: 29392731
- PMCID: PMC5904709
- DOI: 10.1111/imm.12902
Immune modulatory effects of statins
Abstract
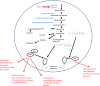
Despite major advances in recent years, immunosuppressive regimens for multiple sclerosis, rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus and graft-versus-host disease still have major adverse effects and immunomodulation rather than immune paralysis would be desirable. Statins inhibit the rate-limiting enzyme of the l-mevalonate pathway, the 3-hydroxy-3-methyl-glutaryl-coenzyme A reductase. It was shown that blocking the l-mevalonate pathway reduces inflammation through effects on downstream metabolites of the pathway including farnesylpyrophosphates and geranylgeranylpyrophosphates, which are essential for the attachment of GTPases like RhoA, Rac and Ras to the cell membrane. Therefore, l-mevalonate pathway downstream products play critical roles in the different steps of an immune response including immune cell activation, migration, cytokine production, immune metabolism and survival. This review discusses the relevance of the different metabolites for the immunomodulatory effect of statins and connects preclinical results with data from clinical studies that tested statins for the treatment of different inflammatory diseases.
Keywords: T helper type 2; inflammation; tolerance; transplantation.
© 2018 John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures
References
-
- Youssef S, Stuve O, Patarroyo JC, Ruiz PJ, Radosevich JL, Hur EM et al The HMG‐CoA reductase inhibitor, atorvastatin, promotes a Th2 bias and reverses paralysis in central nervous system autoimmune disease. Nature 2002; 420:78–84. - PubMed
-
- Leung BP, Sattar N, Crilly A, Prach M, McCarey DW, Payne H et al A novel anti‐inflammatory role for simvastatin in inflammatory arthritis. J Immunol 2003; 170:1524–30. - PubMed
-
- Broady R, Levings MK. Graft‐versus‐host disease: suppression by statins. Nat Med 2008; 14:1155–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

