Early childhood growth and cognitive outcomes: Findings from the MAL-ED study
- PMID: 29392824
- PMCID: PMC6866087
- DOI: 10.1111/mcn.12584
Early childhood growth and cognitive outcomes: Findings from the MAL-ED study
Abstract
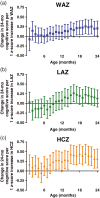
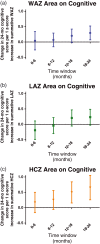
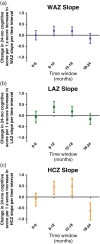
Although many studies around the world hope to measure or improve developmental progress in children to promote community flourishing and productivity, growth is sometimes used as a surrogate because cognitive skills are more difficult to measure. Our objective was to assess how childhood measures of anthropometry correlate with measures of child development in low-income settings with high prevalence of poor nutrition and enteric disease, to inform studies considering growth outcomes in the absence of direct child developmental skill assessment. Children from the MAL-ED study were followed from birth to 24 months of age in field sites in 8 low- and middle-income countries across 3 continents. Monthly weight, length, and head circumference measurements were performed. At 24 months, the Bayley Scales of Infant and Toddler Development was administered. We correlated cognitive measures at 24 months with anthropometric measurements from birth to 2 years comparing 3 constructs: absolute attained monthly measures, summative difference in measures from the mean growth curve, and rate of change in measures. Growth faltering at multiple time periods is related to Bayley cognitive outcomes at 24 months. Birthweight, overall growth by 18-24 months, and rate of growth in the 6- to 18-month period were most associated with 24-month developmental scores. In this study, head circumference measurements, compared with length, was more closely linked to cognitive scores at 24 months. Notably, all studies between growth and cognitive outcomes exhibited low r2 values (0.001-0.049). Anthropometric measures, particularly head circumference, were related to cognitive development, although explaining a low percent of variance. When feasible, direct measures of child development may be more useful.
Keywords: cognition; early childhood development; global health; growth; malnutrition; stunting.
© 2018 John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Alamo‐Junquera, D. , Sunyer, J. , Iniguez, C. , Ballester, F. , Garcia‐Esteban, R. , Forns, J. , … Julvez, J. (2014). Prenatal head growth and child neuropsychological development at age 14 months. American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology, 212(5), 661. e1‐11. - PubMed
-
- American Academy of Pediatrics (2015) Bright futures: Prevention and health promotion for infants, children, adolescents, and their families In: Bright futures. (ed American Academy of Pediatrics ). American Academy of Pediatrics, Elk Grove, IL.
-
- Barker, D. J. P. (2006). Adult consequences of fetal growth restriction. Clinical Obstetrics and Gynecology, 49, 270–283. - PubMed
-
- Bayley, N. (2006). Bayley Scales of Infant and Toddler Development. San Antonio, TX: The Psychological Corporation.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

