β-glucans and cholesterol (Review)
- PMID: 29393350
- PMCID: PMC5810204
- DOI: 10.3892/ijmm.2018.3411
β-glucans and cholesterol (Review)
Abstract
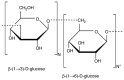
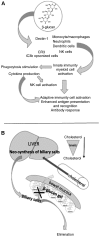
Hypercholesterolemia is one of primary risk factors of cardiovascular disease, together with metabolic syndrome, hypertension and diabetes. Although progress has been made, the search for novel methods of preventing and treating dyslipidemia is ongoing and current therapies for cardiovascular disease induce various side effects. β‑glucans are linear unbranched polysaccharides found in various natural sources, such as mushrooms. Due to their structure they are able to interact with innate immunity receptors, however they also act as dietary fibers in the digestive tract. As there are two forms of β‑glucans, insoluble and soluble forms, they are able to interact with lipids and biliary salts in the bowel and consequently reduce cholesterol levels. Therefore, they may be developed as a suitable therapeutic option to treat patients with dyslipidemia, as they are natural molecules that do not induce any significant side effects. The current review discusses the evidence supporting the effects of β‑glucans on cholesterol levels.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization . Cardiovascular disease. 2016.
-
- World Health Organization . Obesity and overweight fact sheet. 2017.
-
- World Health Organization . Obesity and overweight fact sheet. 2016.
-
- CDC, National Center for Chronic Disease Prevention and Health Promotion and Division for Heart Disease and Stroke Prevention . Heart Disease Facts and Statistics. CDC;
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

