Primaquine or other 8-aminoquinolines for reducing Plasmodium falciparum transmission
- PMID: 29393511
- PMCID: PMC5815493
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD008152.pub5
Primaquine or other 8-aminoquinolines for reducing Plasmodium falciparum transmission
Abstract
Background: The 8-aminoquinoline (8AQ) drugs act on Plasmodium falciparum gametocytes, which transmit malaria from infected people to mosquitoes. In 2012, the World Health Organization (WHO) recommended a single dose of 0.25 mg/kg primaquine (PQ) be added to malaria treatment schedules in low-transmission areas or those with artemisinin resistance. This replaced the previous recommendation of 0.75 mg/kg, aiming to reduce haemolysis risk in people with glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency, common in people living in malarious areas. Whether this approach, and at this dose, is effective in reducing transmission is not clear.
Objectives: To assess the effects of single dose or short-course PQ (or an alternative 8AQ) alongside treatment for people with P. falciparum malaria.
Search methods: We searched the Cochrane Infectious Diseases Group Specialized Register; the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL), published in the Cochrane Library; and the WHO International Clinical Trials Registry Platform (ICRTP) portal using 'malaria*', 'falciparum', 'primaquine', '8-aminoquinoline', and eight 8AQ drug names as search terms. We checked reference lists of included trials, and contacted researchers and organizations. Date of last search: 21 July 2017.
Selection criteria: Randomized controlled trials (RCTs) or quasi-RCTs in children or adults, adding PQ (or alternative 8AQ) as a single dose or short course alongside treatment for P. falciparum malaria.
Data collection and analysis: Two authors screened abstracts, applied inclusion criteria, and extracted data. We sought evidence on transmission (community incidence), infectiousness (people infectious and mosquitoes infected), and potential infectiousness (gametocyte measures assessed by microscopy or polymerase chain reaction [PCR]). We grouped trials into artemisinin and non-artemisinin treatments, and stratified by PQ dose (low, 0.2 to 0.25 mg/kg; moderate, 0.4 to 0.5 mg/kg; high, 0.75 mg/kg). We used GRADE, and absolute effects of infectiousness using trial control groups.
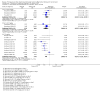
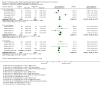
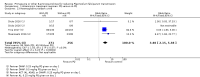
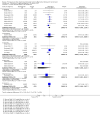
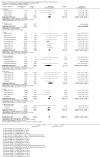
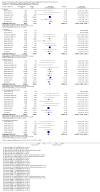
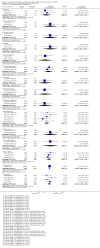
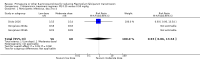
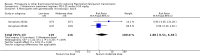
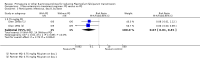
Main results: We included 24 RCTs and one quasi-RCT, comprising 43 arms. Fourteen trials evaluated artemisinin treatments (23 arms), nine trials evaluated non-artemisinin treatments (13 arms), and two trials included both artemisinin and non-artemisinin arms (three and two arms, respectively). Two trial arms used bulaquine. Seven PQ arms used low dose (six with artemisinin), 11 arms used moderate dose (seven with artemisinin), and the remaining arms used high dose. Fifteen trials tested for G6PD status: 11 excluded participants with G6PD deficiency, one included only those with G6PD deficiency, and three included all, irrespective of status. The remaining 10 trials either did not test or did not report on testing.No cluster trials evaluating community effects on malaria transmission met the inclusion criteria.With artemisinin treatmentLow dose PQInfectiousness (participants infectious to mosquitoes) was reduced (day 3 or 4: RR 0.12, 95% CI 0.02 to 0.88, 3 trials, 105 participants; day 8: RR 0.34, 95% CI 0.07 to 1.58, 4 trials, 243 participants; low certainty evidence). This translates to a reduction in percentage of people infectious on day 3 or 4 from 14% to 2%, and, for day 8, from 4% to 1%; the waning infectiousness in the control group by day 8 making the absolute effect smaller by day 8. For gametocytes detected by PCR, there was little or no effect of PQ at day 3 or 4 (RR 1.02, 95% CI 0.87 to 1.21; 3 trials, 414 participants; moderate certainty evidence); with reduction at day 8 (RR 0.52, 95% CI 0.41 to 0.65; 4 trials, 532 participants; high certainty evidence). Severe haemolysis was infrequent, with or without PQ, in these groups with few G6PD-deficient individuals (RR 0.98, 95% CI 0.69 to 1.39; 4 trials, 752 participants, moderate certainty evidence).Moderate dose PQInfectiousness was reduced (day 3 or 4: RR 0.13, 95% CI 0.02 to 0.94; 3 trials, 109 participants; day 8 RR 0.33, 95% CI 0.07 to 1.57; 4 trials, 246 participants; low certainty evidence). Illustrative risk estimates for moderate dose were the same as low dose. The pattern and level of certainty of evidence with gametocytes detected by PCR was the same as low dose, and severe haemolysis was infrequent in both groups.High dose PQInfectiousness was reduced (day 4: RR 0.2, 95% CI 0.02 to 1.68, 1 trial, 101 participants; day 8: RR 0.18, 95% CI 0.02 to 1.41, 2 trials, 181 participants, low certainty evidence). The effects on gametocyte prevalence showed a similar pattern to moderate and low dose PQ. Trials did not systematically report evidence of haemolysis.With non-artemisinin treatmentTrials with non-artemisinin treatment have been conducted only for moderate and high dose PQ. With high dose, infectiousness appeared markedly reduced on day 5 (RR 0.09, 95% CI 0.01 to 0.62; 30 participants, very low certainty evidence), with similar reductions at day 8. For both moderate dose (two trials with 221 people) and high dose (two trials with 30 people), reduction in gametocytes (detected by microscopy) showed similar patterns as for artemisinin treatments, with little or no effect at day 4 or 5, and larger effects by day 8. No trials with non-artemisinin partner drugs systematically sought evidence of severe haemolysis.Two trials comparing bulaquine with PQ suggest bulaquine may have larger effects on gametocytes by microscopy on day 8 (RR 0.41, 95% CI 0.26 to 0.66; 2 trials, 112 participants).
Authors' conclusions: A single low dose of PQ (0.25 mg/kg) added to artemisinin-based combination therapy for malaria reduces infectiousness of people to mosquitoes at day 3-4 and day 8, and appears as effective as higher doses. The absolute effect is greater at day 3 or 4, and smaller at day 8, in part because of the lower infectiousness in the control group. There was no evidence of increased haemolysis at 0.25 mg/kg, but few G6PD-deficient individuals were included in the trials. The effect on infectiousness precedes the effect of PQ on gametocyte prevalence. We do not know whether single dose PQ could reduce malaria transmission at community level.
Conflict of interest statement
We have no affiliations with or involvement in any organization or entity with a direct financial interest in the subject matter of the review (for example, employment, consultancy, stock ownership, honoraria, or expert testimony).
This review and the salary of PG is supported by a DFID grant aimed at ensuring the best possible systematic reviews, particularly Cochrane Reviews, are completed on topics relevant to the poor in low‐ and middle‐income countries. DFID does not participate in the selection of topics, in the conduct of the review or in the interpretation of findings. PG is a member of the WHO Guidelines for the Treatment of Malaria Group that made the recommendation for PQ to reduce
PMG was a member from 2012 to 2016 of the WHO Malaria Policy Advisory Committee, which provides independent strategic advice in forming WHO policies in malaria.
HG and LC have no known conflicts of interest.
None of the review authors are investigators on any of the included trials.
Figures

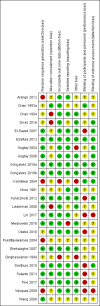
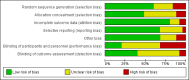
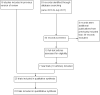




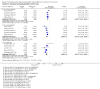
















Update of
-
Primaquine or other 8-aminoquinoline for reducing Plasmodium falciparum transmission.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Feb 19;(2):CD008152. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008152.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Feb 02;2:CD008152. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008152.pub5. PMID: 25693791 Free PMC article. Updated.
References
References to studies included in this review
Arango 2012 {published data only}
-
- Arango EA, Upegui UA, Carmona‐Fonseca J. Efficacy of different primaquine‐based antimalarial regimens against Plasmodium falciparum gametocytemia. Acta Tropica 2012;122(2):177‐82. - PubMed
Chen 1993a {published data only}
-
- Chen PQ, Li GQ, Guo XB, Fu YX, He KR, Fu LC, et al. A double blind study on the infectivity of gametocytes of P. falciparum in patients treated with mefloquine and Fansimef. Journal of Guangzhou College of Traditional Chinese Medicine 1993;10(1):1‐5.
Chen 1994 {published data only}
-
- Chen PQ, Li GQ, Guo XB. The infectivity of gametocytes of Plasmodium falciparum from patients treated with artemisinin [Chinese]. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi 1994;74(4):209‐10, 253‐4. - PubMed
-
- Chen PQ, Li GQ, Guo XB, He KR, Fu YX, Fu LC, et al. The infectivity of gametocytes of Plasmodium falciparum from patients treated with artemisinin. Chinese Medical Journal 1994;107(9):709‐11. - PubMed
Dicko 2016 {published data only}
-
- Dicko A, Brown JM, Diawara H, Baber I, Mahamar A, Soumare HM, et al. Primaquine to reduce transmission of Plasmodium falciparum malaria in Mali: a single‐blind, dose‐ranging, adaptive randomised phase 2 trial. Lancet. Infectious Diseases 2016;16(6):674‐84. [DOI: 10.1016/s1473-3099(15)00479-x] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
El‐Sayed 2007 {published data only}
-
- El‐Sayed B, El‐Zaki SE, Babiker H, Gadalla N, Ageep T, Mansour F, et al. A randomized open‐label trial of artesunate‐sulfadoxine‐pyrimethamine with or without primaquine for elimination of sub‐microscopic P. falciparum parasitaemia and gametocyte carriage in eastern Sudan. PLoS One 2007;2(12):e1311. - PMC - PubMed
Eziefula 2013 {published data only}
-
- Eziefula AC, Bousema T, Yeung S, Kamya M, Owaraganise A, Gabagaya G, et al. Single dose primaquine for clearance of Plasmodium falciparum gametocytes in children with uncomplicated malaria in Uganda: a randomised, controlled, double‐blind, dose‐ranging trial. Lancet. Infectious Diseases 2013;14(2):130‐9. - PubMed
-
- Eziefula AC, Pett H, Grignard H, Opus S, Kiggundu M, Kamya MR, et al. Glucose‐6‐phosphate dehydrogenase status and risk of hemolysis in Plasmodium falciparum‐infected African children receiving single‐dose primaquine. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 2014;58(8):4971‐3. [DOI: 10.1128/aac.02889-14] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Eziefula AC, Staedke SG, Yeung S, Webb E, Kamya M, White NJ, et al. Study protocol for a randomised controlled double‐blinded trial of the dose‐dependent efficacy and safety of primaquine for clearance of gametocytes in children with uncomplicated falciparum malaria in Uganda. BMJ Open 2013;3(3):e002759. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Pett H, Drakeley C, Eziefula C, Neuvonen M, Lanke K, Sauerwein R, et al. CYP2D6 intermediate metabolizer status could slow down Plasmodium falciparum gametocyte clearance after single‐dose primaquine. Malaria Journal 2014;13(Suppl 1):P69.
Gogtay 2004 {published data only}
-
- Gogtay NJ, Kamtekar KD, Dalvi SS, Chogle AR, Aigal U, Kshirsagar N. Preliminary report of the evaluation of the gametocytocidal action of bulaquine, in adult patients with acute, Plasmodium falciparum malaria. Annals of Tropical Medicine and Parasitology 2004;98(5):525‐8. - PubMed
Gogtay 2006 {published data only}
-
- Gogtay NJ, Kamtekar KD, Dalvi SS, Mehta SS, Chogle AR, Aigal U, et al. A randomized, parallel study of the safety and efficacy of 45 mg primaquine versus 75 mg bulaquine as gametocytocidal agents in adults with blood schizonticide‐responsive uncomplicated falciparum malaria [ISCRTN50134587]. BMC Infectious Diseases 2006;6:16. - PMC - PubMed
Gonçalves 2016a {published data only}
-
- Gonçalves BP, Tiono AB, Ouédraogo A, Guelbéogo WM, Bradley J, Nebie I, et al. Single low dose primaquine to reduce gametocyte carriage and Plasmodium falciparum transmission after artemether‐lumefantrine in children with asymptomatic infection: a randomised, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled trial. BMC Medicine 2016;14:40. - PMC - PubMed
Gonçalves 2016b {published data only}
-
- Gonçalves BP, Tiono AB, Ouédraogo A, Guelbéogo WM, Bradley J, Nebie I, et al. Single low dose primaquine to reduce gametocyte carriage and Plasmodium falciparum transmission after artemether‐lumefantrine in children with asymptomatic infection: a randomised, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled trial. BMC Medicine 2016;14:40. - PMC - PubMed
Kamtekar 2004 {published data only}
-
- Kamtekar KD, Gogtay NJ, Dalvi SS, Karnad DR, Chogle AR, Aigal U, et al. A prospective study evaluating the efficacy of a single, 45‐mg dose of primaquine, as a gametocytocidal agent, in patients with Plasmodium falciparum malaria in Mumbai, India. Annals of Tropical Medicine and Parasitology 2004;98(5):453‐8. - PubMed
Khoo 1981 {published data only}
-
- Khoo KK. The treatment of malaria in glucose‐6‐phosphate dehydrogenase deficient patients in Sabah. Annals of Tropical Medicine and Parasitology 1981;75(6):591‐5. - PubMed
Kolaczinski 2012 {published data only}
Lederman 2006 {published data only}
Lin 2017 {published data only}
-
- Spring M, Lon C, Manning J, Vanachayangul P, Chaorattanakawee S, Gosi P, et al. Evaluation of dihydroartemisinin‐piperaquine with and without single dose primaquine: an open‐label randomized, controlled trial in Anlong Veng, Cambodia. American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene 2014;91(5 Suppl 1):276‐7.
-
- Spring MD, Lin JT, Manning JE, Vanachayangkul P, Somethy S, Bun R, et al. Dihydroartemisinin‐piperaquine failure associated with a triple mutant including kelch13 C580Y in Cambodia: an observational cohort study. Lancet. Infect Diseases 2015;15(6):686‐91. [DOI: 10.1016/S1473-3099(15)70049-6.] - DOI - PubMed
Mwaiswelo 2016 {published data only}
-
- Mwaiswelo R, Ngasala BE, Jovel I, Aydin‐Schmidt B, Gosling R, Premji Z, et al. Adding a single low‐dose of primaquine (0.25 mg/kg) to artemether‐lumefantrine did not compromise treatment outcome of uncomplicated Plasmodium falciparum malaria in Tanzania: a randomized, single‐blinded clinical trial. Malaria Journal 2016;15(1):435. - PMC - PubMed
Okebe 2016 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Okebe J, Bousema T, Affara M, Tanna GL, Dabira E, Gaye A, et al. The gametocytocidal efficacy of different single doses of primaquine with dihydroartemisinin‐piperaquine in asymptomatic parasite carriers in The Gambia: a randomized controlled trial. EBioMedicine 2016;13:348‐55. [DOI: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2016.10.032] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Okebe J, Bousema T, Affara M, DiTanna, Eziefula AC, Jawara M, et al. The gametocytocidal efficacy of primaquine in malaria asymptomatic carriers treated with dihydroartemisinin‐piperaquine in The Gambia (PRINOGAM): study protocol for a randomised controlled trial. Trials 2015;16:70. [DOI: 10.1186/s13063-015-0597-1] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Pukrittayakamee 2004 {published data only}
Shekalaghe 2007 {published and unpublished data}
Singhasivanon 1994 {published data only}
-
- Singhasivanon V, Chongsuphajaisiddhi T, Sabchareon A, Attanath P, Webster HK, Edstein MD, et al. Pharmacokinetic study of mefloquine in Thai children aged 5‐12 years suffering from uncomplicated falciparum malaria treated with MSP or MSP plus primaquine. European Journal of Drug Metabolism and Pharmacokinetics 1994;19(1):27‐32. - PubMed
Smithuis 2010 {published and unpublished data}
Sutanto 2013 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Sutanto I, Suprijanto S, Kosasih A, Dahlan MS, Syafruddin D, Kusriastuti R, et al. The effect of primaquine on gametocyte development and clearance in the treatment of uncomplicated falciparum malaria with dihydroartemisinin‐piperaquine in South Sumatra, Western Indonesia: an open‐label, randomized, controlled trial. Clinical Infectious Diseases 2013;56(5):685–93. - PubMed
Tine 2017 {published data only}
-
- Tine RC, Sylla K, Faye BT, Poirot E, Fall FB, Sow D, et al. Safety and efficacy of adding a single low dose of primaquine to the treatment of adult patients with Plasmodium falciparum malaria in Senegal, to reduce gametocyte carriage: a randomized controlled trial. Clinical Infectious Diseases 2017;65(4):535‐43. - PMC - PubMed
Vásquez 2009 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Vásquez AM, Sanín F, Alvarez LG, Tobón A, Ríos A, Blair S. Therapeutic efficacy of a regimen of artesunate‐mefloquine‐primaquine treatment for Plasmodium falciparum malaria and treatment effects on gametocytic development [Estudio piloto de la eficacia y de los efectos sobre los gametocitos del esquema artesunato‐mefloquina‐primaquina para la malaria por Plasmodium falciparum]. Biomedica 2009;29(2):307‐19. - PubMed
Wang 2006 {published data only}
-
- Wang YS, Brown PP. Clinical study on artemether combined with Primaquine for Pf cases treatment [Chinese]. Tianjin Medical Journal 2006;34(8):538.
References to studies excluded from this review
Baird 2002 {published data only}
-
- Baird JK, Wiady I, Sutanihardja A, Suradi, Purnomo, Basri H, et al. Short report: therapeutic efficacy of chloroquine combined with primaquine against Plasmodium falciparum in northeastern Papua, Indonesia. American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene 2002;66(6):659‐60. - PubMed
Barber 1929 {published data only}
-
- Barber MA, Komp WHW, Newman BM. The effect of small doses of plasmochin on the viability of gametocytes of malaria as measured by mosquito infection experiments. Public Health Reports 1929;44(24):1409‐20.
Barber 1932 {published data only}
-
- Barber MA, Rice JB, Brown JY. Malaria studies on the Firestone Rubber Plantation in Liberia, West Africa. American Journal of Hygiene 1932;15(3):601‐33.
Brueckner 1998 {published data only}
-
- Brueckner RP, Lasseter KC, Lin ET, Schuster BG. First‐time‐in‐humans safety and pharmacokinetics of WR 238605, a new antimalarial. American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene 1998;58(5):645‐9. - PubMed
Bunnag 1980 {published data only}
-
- Bunnag D, Harinasuta T, Pinichpongse S, Suntharasamai P. Effect of primaquine on gametocytes of Plasmodium falciparum in Thailand. Lancet 1980;2(8185):91. - PubMed
Burgess 1961 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Burgess RW, Bray RS. The effect of a single dose of primaquine upon the gametocytes, gametogony and sporogony of Laverania (= Plasmodium) falciparum. WHO/MAL/271. 24 August 1960. http://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/10665/64747/1/WHO_Mal_271.pdf?ua=1 (accessed 15 January 2018). - PMC - PubMed
Cai 1985 {published data only}
-
- Cai XZ, Yang XP, He XZ, Zhan WC, Zhan X, Ye BS. The combined use of artemether, sulfadoxine, pyrimethamine and primaquine in the treatment of chloroquine‐resistant falciparum malaria. Ji Sheng Chong Xue Yu Ji Sheng Chong Bing Za Zhi [Chinese Journal of Parasitology and Parasitic Diseases] 1985;3(2):81‐4. - PubMed
Carter 2011 {published data only}
Che 1987 {published data only}
-
- Che LG, Huang KG, Yang HL, Yu L, Lin ZL, Huang R. Combined use of pyronaridine, sulfadoxine and primaquine in areas with chloroquine‐resistant falciparum malaria. Zhongguo Ji Sheng Chong Xue Yu Ji Sheng Chong Bing Za Zhi [Chinese Journal of Parasitology and Parasitic Diseases] 1987;5(3):194‐6. - PubMed
Che 1990 {published data only}
-
- Che L, Huang K, Dong Y, Yang H, Yang P. Efficacy of two combined therapies for treatment of chloroquine‐resistant P. falciparum. Chinese Journal of Parasitic Disease Control 1990;3(1):24‐6.
Chevalley 2010 {published data only}
Clyde 1962 {published data only}
Clyde 1970 {published data only}
-
- Clyde DF, DuPont HL, Miller RM, McCarthy VC. Prophylactic and sporontocidal treatment of chloroquine resistant Plasmodium falciparum from Malaya. Transactions of the Royal Society of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene 1970;64(6):834‐8. - PubMed
Clyde 1971 {published data only}
-
- Clyde DF, Miller RM, Music SI, McCarthy VC. Prophylactic and sporontocidal treatment of chloroquine‐resistant Plasmodium falciparum from Vietnam. American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene 1971;20(1):1‐5. - PubMed
da Silva 1984 {published data only}
-
- Silva AR, Carneiro EW, dos Santos HJ. Response of human Plasmodium to antimalarials on the Island of Saint Louis, State of Maranhão, Brazil. Revista do Instituto de Medecina Tropical de São Paulo 1984;26(3):139‐46. - PubMed
Degowin 1966 {published data only}
Doi 1989 {published data only}
-
- Doi H, Kaneko A, Panjaitan W, Ishii A. Chemotherapeutic malaria control operation by single dose of Fansidar plus primaquine in North Sumatra, Indonesia. Southeast Asian Journal of Tropical Medicine and Public Health 1989;20(3):341‐9. - PubMed
Giao 2004 {published data only}
-
- Giao PT, Vries PJ, Hung le Q, Binh TQ, Nam NV, Kager PA. CV8, a new combination of dihydroartemisinin, piperaquine, trimethoprim and primaquine, compared with atovaquone‐proguanil against falciparum malaria in Vietnam. Tropical Medicine & International Health 2004;9(2):209‐16. - PubMed
Gogtay 1999 {published data only}
-
- Gogtay NJ, Chogle AR, Sorabjee JS, Marathe SN, Kshirsagar NA. Poor gametocytocidal activity of 45 mg primaquine in chloroquine‐treated patients with acute, uncomplicated, Plasmodium falciparum malaria in Mumbai (Bombay): an issue of public‐health importance. Annals of Tropical Medicine and Parasitology 1999;93(8):813‐6. - PubMed
Gunders 1961 {published data only}
Hii 1987 {published data only}
-
- Hii JL, Vun YS, Chin KF, Chua R, Tambakau S, Binisol ES, et al. The influence of permethrin‐impregnated bednets and mass drug administration on the incidence of Plasmodium falciparum malaria in children in Sabah, Malaysia. Medical and Veterinary Entomology 1987;1(4):397‐407. - PubMed
Huang 1993 {published data only}
-
- Huang ZS, Fu SG, Cai XZh. Combined use of pyronaridine/SP with primaquine for P. falciparum treatment. Journal of Hainan Medicine 1993;4(1):10‐2.
Huang 1996 {published data only}
-
- Huang Z, Meng F, Fu S. Comparative studies on the treatment of drug‐resistant P. falciparum with pyronaridine/SP and primaquine. Zhongguo Ji Sheng Chong Xue Yu Ji Sheng Chong Bing Za Zhi [Chinese Journal Parasitology and Parasitic Diseases] 1996;14(4):314‐7.
Huang 2001 {published data only}
-
- Huang JR, Gao YQ, Elie N. A study of artemether combined with primaquine in the treatment of falciparum malaria. Zhongguo Ji Sheng Chong Xue Yu Ji Sheng Chong Bing Za Zhi [Chinese Journal of Parasitology and Parasitic Diseases] 2001;19(5):308‐9. - PubMed
Jeffery 1956 {published data only}
-
- Jeffery GM, Young MD, Eyles DE. The treatment of Plasmodium falciparum infection with chloroquine, with a note on infectivity to mosquitoes of primaquine‐ and pyrimethamine‐treated cases. American Journal of Hygiene 1956;64(1):1‐11. - PubMed
Jeffery 1963 {published data only}
-
- Jeffery GM, Collins WE, Skinner JC. Antimalarial drug trials on a multiresistant strain of Plasmodium falciparum. American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene 1963;12:844‐50. - PubMed
Jerace 1933 {published data only}
-
- Jerace F, Giovannola A. The sterilizing action of plasmochina on gametocytes of malaria parasites and its prophylactic importance [L'azzione sterilizzante della plasmochina sui gametociti di parassiti malarigeni e sua importanza profilattica]. Rivista di Malariaologia 1933;12:475.
Kaneko 1989 {published data only}
-
- Kaneko A, Kamei K, Suzuki T, Ishii A, Siagian R, Panjaitan W. Gametocytocidal effect of primaquine in a chemotherapeutic malaria control trial in North Sumatra, Indonesia. Southeast Asian Journal of Tropical Medicine and Public Health 1989;20(3):351‐9. - PubMed
Karbwang 1991 {published data only}
-
- Karbwang J, Molunto P, Bunnag D, Harinasuta T. Plasma quinine levels in patients with falciparum malaria when given alone or in combination with tetracycline with or without primaquine. Southeast Asian Journal of Tropical Medicine and Public Health 1991;22(1):72‐6. - PubMed
Karbwang 1992 {published data only}
-
- Karbwang J, Na Bangchang K, Thanavibul A, Back DJ, Bunnag D. Pharmacokinetics of mefloquine in the presence of primaquine. European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 1992;42(5):559‐60. - PubMed
Kyaw 1994 {published data only}
-
- Myat‐Phone‐Kyaw, Myint‐Oo, Aung‐Naing, Aye‐Lwin‐Htwe. The use of primaquine in malaria infected patients with red cell glucose phosphate (G6PD) deficiency in Myanmar. Southeast Asian Journal of Tropical Medicine and Public Health 1994;25(4):710‐3. - PubMed
Li 2007 {published data only}
-
- Li J, Xiao H, Wang W, Ma W, Rao B. Artemether combined with primaquine for P. falciparum cases treatment. Clinical Medical Journal of China 2007;14(5):736‐7.
Li 2010 {published data only}
-
- Li WJ, Li XL. Observation of curative effect of falciparum malaria treatment with artemether/lumefantrine and primaquine. Journal of Modern Preventive Medicine 2010;37(5):973‐5.
Lin 2004 {published data only}
-
- Lin L, Wang D‐L, Liu B, Hu G. Artemether combined with primaquine for treatment of malaria cases from UN peace force. Chinese Journal of Parasitic Disease Control 2004;17(5):5‐6.
Mackerras 1949 {published data only}
-
- Mackerras MJ, Ercole QN. Observations on the action of quinine, atebrin and plasmoquine on the gametocytes of Plasmodium falciparum. Transactions of the Royal Society of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene 1949;42(5):455‐63. - PubMed
Mapanawang 2016 {published data only}
-
- Mapanawang AL, Mustofa, Wijayanti MA, Handayani R, Mogi Y, Mapanawang F, et al. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of primaquine to patients with uncomplicated falciparum malaria in Halmahera Indonesia. International Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences and Research 2016;7(4):1430‐40. [DOI: 10.13040/IJPSR.0975-8232.7%284%29.1430-40] - DOI
Rieckmann 1968 {published data only}
-
- Rieckmann KH, McNamara JV, Frischer H, Stockert TA, Carson PE, Powell RD. Gametocytocidal and sporontocidal effects of primaquine and of sulfadiazine with pyrimethamine in a chloroquine‐resistant strain of Plasmodium falciparum. Bulletin of the World Health Organization 1968;38(4):625–32. - PMC - PubMed
Rieckmann 1969 {published data only}
-
- Rieckmann KH, McNamara JV, Kass L, Powell RD. Gametocytocidal and sporontocidal effects of primaquine upon two strains of Plasmodium falciparum. Military Medicine 1969;134(10):802‐19. - PubMed
Santana 2007 {published data only}
-
- Santana MS, Rocha MA, Arcanjo AR, Sardinha JF, Alecrim WD, Alecrim Md. Association of methemoglobinemia and glucose‐6‐phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency in malaria patients treated with primaquine [Associação de metemoglobinemia e deficiência de glicose‐6‐fosfato desidrogenase em pacientes com malária tratados com primaquina]. Revista da Sociedade de Brasileira de Medicina Tropical 2007;40(5):533‐6. - PubMed
Shah 2013 {published data only}
-
- Shah NK, Schapira A, Juliano JJ, Srivastava B, MacDonald PD, Poole C, et al. Nonrandomized controlled trial of artesunate plus sulfadoxine‐pyrimethamine with or without primaquine for preventing posttreatment circulation of Plasmodium falciparum gametocytes. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 2013;57(7):2948‐54. - PMC - PubMed
Shekalaghe 2010 {published data only}
-
- Shekalaghe SA, ter Braak R, Daou M, Kavishe R, Bijllaardt W, Bosch S, et al. In Tanzania, hemolysis after a single dose of primaquine coadministered with an artemisinin is not restricted to glucose‐6‐phosphate dehydrogenase‐deficient (G6PD A‐) individuals. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 2010;54(5):1762‐8. - PMC - PubMed
Shekalaghe 2011 {published data only}
Sun 2011 {published data only}
-
- Sun W‐H, Traore A. Artesunate combined with primaquine in treatment study on delay or relapse of malaria. Chinese Journal of Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics 2011;1:98‐100.
Suputtamongkol 2003 {published data only}
-
- Suputtamongkol Y, Chindarat S, Silpasakorn S, Chaikachonpatd S, Lim K, Chanthapakajee K, et al. The efficacy of combined mefloquine‐artesunate versus mefloquine‐primaquine on subsequent development of Plasmodium falciparum gametocytemia. American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene 2003;68(5):620‐3. - PubMed
Tangpukdee 2008 {published data only}
Yang 1989 {published data only}
-
- Yang H, Che L, Huang K, Yang P, Dong Y, Lin Z, et al. The effect of combinations of pyronaridine, sufadoxine and primaquine on chloroquine‐resistant P. falciparum. Chinese Journal of Parasitic Disease Control 1989;2(1):7‐10.
Yeramian 2005 {published data only}
-
- Yeramian P, Meshnick SR, Krudsood S, Chalermrut, K, Silachamroon U, Tangpukdee N, et al. Efficacy of DB289 in Thai patients with Plasmodium vivax or acute, uncomplicated Plasmodium falciparum infections. Journal of Infectious Diseases 2005;192(2):319‐22. - PubMed
Young 1959 {published data only}
-
- Young MD. The effect of small doses of primaquine upon malaria infections. Indian Journal of Malariology 1959;13:69–74.
References to studies awaiting assessment
Chen 1993b {published data only}
-
- Chen L. Efficacy of artemether/primaquine against drug resistant P. falciparum [Chinese]. Journal of Applied Medicine 1993;1(1):31‐3.
Ishii 2009 {unpublished data only}
-
- Ishii A, Ohta N, Owhashi M, Kawabata M, Chung D, Bobogare A, et al. Trials of transmission blocking of P. falciparum with single dose primaquine in villages of Solomon Islands. MIM conference October 2009 MIM 16723361.
Li 2006 {published data only}
-
- Li J, et al. Artemether combined with primaquine for treatment of 50 Pf cases [Chinese]. Journal of Applied Medicine 2006;22(19):2299‐300.
References to ongoing studies
ISRCTN11594437 {unpublished data only}
-
- ISRCTN11594437. Primaquine in African Children (PAC study) [Assessing the tolerability and safety of single low dose primaquine in African children with acute uncomplicated falciparum malaria and glucose 6 phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency in Africa.]. isrctn.com/ISRCTN11594437 (first received 09/05/2017).
NCT01906788 {unpublished data only}
-
- NCT01906788. The optimal timing of primaquine to prevent malaria transmission after artemisinin‐combination therapy. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01906788 (first posted 24 July 2013).
NCT02259426 {unpublished data only}
-
- NCT02259426. Dihydroartemisinin‐piperaquine with low dose primaquine to reduce malaria transmission (DAPPI). clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02259426 (first posted 8 October 2014).
NCT02431650 {unpublished data only}
-
- NCT02431650. Effectiveness of OZ439 as a gametocytocidal and transmission blocking agent (OZGAM) [A proof‐of‐concept study to assess the effectiveness of OZ439 as a gametocytocidal and transmission blocking agent in experimental P. falciparum infection]. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02431650 (first posted 1 May 2015).
NCT02434952 {unpublished data only}
-
- NCT02434952. Safety and tolerability of low dose primaquine. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02434952 (first posted 6 May 2015).
NCT02831023 {unpublished data only}
-
- NCT02831023. Phase 2 efficacy study of primaquine and methylene blue. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02831023 (first posted 13 July 2016).
NCT02851108 {unpublished data only}
-
- NCT02851108. Methylene blue against falciparum malaria in Burkina Faso (BlueACTn) [Safety of artesunate‐amodiaquine combined with methylene blue or primaquine for falciparum malaria treatment in African children: a randomised controlled trial]. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02851108 (first posted 1 August 2016).
PACTR201611001859416 {unpublished data only}
-
- PACTR201611001859416. Addition of low dose primaquine to artemether‐lumefantrine for the treatment of uncomplicated malaria [A randomised controlled trial to investigate the efficacy, safety and tolerability of adding a single low primaquine dose to artemether‐lumefantrine for the treatment of symptomatic uncomplicated Plasmodium falciparum malaria]. www.pactr.org/ATMWeb/appmanager/atm/atmregistry?dar=true&tNo=PACTR20... (date of registration 11 November 2016).
Additional references
Abay 2013
Arnold 1955
-
- Arnold J, Alving AS, Hockwald RS, Clayman CB, Dern RJ, Beutler E, et al. The antimalarial action of primaquine against the blood and tissue stages of falciparum malaria (Panama, P‐F‐6 strain). Journal of Laboratory and Clinical Medicine 1955;46(3):391‐7. - PubMed
Ashley 2014
Balshem 2011
Barnes 2008
-
- Barnes KI, Little F, Mabuza A, Mngomezulu N, Govere J, Durrheim D, et al. Increased gametocytemia after treatment: an early parasitological indicator of emerging sulfadoxine‐pyrimethamine resistance in falciparum malaria. Journal of Infectious Diseases 2008;197(11):1605‐13. - PubMed
Bennett 2013
-
- Bennett JW, Pybus BS, Yadava A, Tosh D, Sousa JC, McCarthy WF, et al. Primaquine failure and cytochrome P‐450 2D6 in Plasmodium vivax malaria. New England Journal of Medcine 2013;369(14):1381‐2. - PubMed
Bhasin 1984
-
- Bhasin VK, Trager W. Chapter XI: Gametocytocidal effects in vitro of primaquine and related compounds on Plasmodium falciparum. In: Wernsdorfer WH, Trigg PI editor(s). Primaquine: Pharmacokinetics, Metabolism, Toxicity and Activity. Geneva: UNDP/World Bank/WHO, 1984.
Bousema 2010
Bousema 2011
Bousema 2012
Bousema 2014
Breman 2012
-
- Breman JG. Resistance to artemisinin‐based combination therapy. Lancet. Infectious Diseases 2012;12(11):820‐2. - PubMed
Carter 1988
-
- Carter R, Graves PM. Gametocytes. In: Wernsdorfer WH, MacGregor IA editor(s). Malaria: Principles and Practice of Malariology. Edinburgh: Churchill Livingstone, 1988.
Chotivanich 2006
Churcher 2013
Drakeley 2006
-
- Drakeley C, Sutherland C, Bousema JT, Sauerwein RW, Targett GA. The epidemiology of Plasmodium falciparum gametocytes: weapons of mass dispersion. Trends in Parasitology 2006;22(9):424‐30. - PubMed
Eichner 2001
-
- Eichner M, Diebner HH, Molineaux L, Collins WE, Jeffery GM, Dietz K. Genesis, sequestration and survival of Plasmodium falciparum gametocytes: parameter estimates from fitting a model to malaria therapy data. Transactions of the Royal Society of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene 2001;95(5):497‐501. - PubMed
Eziefula 2012
Gerardin 2015a
Gerardin 2015b
GMAP 2008
-
- Roll Back Malaria Partnership. Global Malaria Action Plan. Geneva: RBM/WHO, 2008.
Graves 1988
-
- Graves PM, Burkot TR, Carter R, Cattani JA, Lagog M, Parker J, et al. Measurement of malarial infectivity of human populations to mosquitoes in the Madang area, Papua New Guinea. Parasitology 1988;96(Pt 2):251‐63. - PubMed
Graves 1990
-
- Graves PM, Burkot TR, Saul AJ, Hayes RJ, Carter R. Estimation of anopheline survival rate, vectorial capacity and mosquito infection probability from malaria infection rates in villages near Madang, Papua New Guinea. Journal of Applied Ecology 1990;27:134‐47.
Guyatt 2011
Hastings 2006
-
- Hasting IM. Gametocytocidal activity in antimalarial drugs speeds the spread of drug resistance. Tropical Medicine & International Health 2006;11(8):1206‐17. - PubMed
Higgins 2011
-
- Higgins JPT, Altman DH, Sterne JAC. Chapter 8: Assessing risk of bias in included studies. In: Higgins JPT, Green S, editor(s). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 (updated March 2011). The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from handbook.cochrane.org.
Howes 2013
Johnston 2014
Kaneko 2000
-
- Kaneko A, Taleo G, Kalkoa M, Yamar S, Kobayakawa T, Björkman A. Malaria eradication on islands. Lancet 2000;356(9241):1560‐4. - PubMed
Killeen 2006
-
- Killeen GF, Ross A, Smith T. Infectiousness of malaria‐endemic human populations to vectors. American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene 2006;75(2 Suppl):38‐45. - PubMed
Lefebvre 2011
-
- Lefebvre C, Manheimer E, Glanville J. Chapter 6: Searching for studies. In: Higgins JP, Green S, editor(s). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 (updated March 2011). The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from handbook.cochrane.org. Chichester.
Lines 1991
-
- Lines JD, Wilkes TJ, Lyimo EO. Human malaria infectiousness measured by age‐specific sporozoite rates in Anopheles gambiae in Tanzania. Parasitology 1991;102(2):167‐77. - PubMed
Meltzer 2014
-
- Meltzer E, Schwartz E. Low‐dose primaquine for falciparum malaria. Lancet. Infectious Diseases 2014;14(6):449. - PubMed
Mendis 2009
-
- Mendis K, Rietveld A, Warsame M, Bosman A, Greenwood B, Wernsdorfer W. From malaria control to eradication: the WHO perspective. Tropical Medicine & International Health 2009;14(7):802‐9. - PubMed
Okell 2008a
Okell 2008b
Olalekan 2017
Ouédraogo 2009
Phillips 2017
Poirot 2013
Price 1996
-
- Price R, Nosten F, Luxemburger C, ter Kuile FO, Paiphun L, Chongsuphajaisiddhi T, et al. The effects of artemisinin derivatives on malaria transmissibility. Lancet 1996;347(9016):1654‐8. - PubMed
RevMan 2014 [Computer program]
-
- Nordic Cochrane Centre. The Cochrane Collaboration. Review Manager 5 (RevMan 5). Version 5.3. Copenhagen: Nordic Cochrane Centre. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2014.
Smalley 1977
-
- Smalley ME, Sinden RE. Plasmodium falciparum gametocytes: their longevity and infectivity. Parasitology 1977;74(1):1‐8. - PubMed
Stone 2015
-
- Stone W, Goncalves BP, Bousema T, Drakeley C. Assessing the infectious reservoir of falciparum malaria, past and future. Trends in Parasitology 2015;31(7):287‐296. - PubMed
Sturrock 2013
von Seidlein 2003
-
- Seidlein L, Greenwood BM. Mass administrations of antimalarial drugs. Trends in Parasitology 2003;19(10):452‐60. - PubMed
White 1992
White 2008
White 2012
White 2013
-
- White NJ. Primaquine to prevent transmission of falciparum malaria. Lancet. Infectious Diseases 2013;13(2):175‐81. - PubMed
White 2014
WHO 2010
-
- World Health Organization. Guidelines for the Treatment of Malaria. 2nd Edition. Geneva: World Health Organization, 2010.
WHO 2012a
-
- World Health Organization. WHO Evidence Review Group: The safety and effectiveness of single dose primaquine as a P. falciparium gametoctyocide. Meeting Report. Geneva: World Health Organization, 2012.
WHO 2012b
-
- Global Malaria Programme, World Health Organization. Single dose primaquine as a gametocytocide in Plasmodium falciparum malaria. Updated WHO Policy Recommendation. Geneva: World Health Organization, 2012.
WHO 2015a
-
- World Health Organization. Policy brief on single dose primaquine as a gametocytocide in Plasmodium falciparum malaria. WHO/HTM/GMP/2015.1. January 2015. www.who.int/malaria/publications/atoz/policy‐brief‐single‐dose‐primaquin... (accessed 16 January 2018).
WHO 2015b
-
- World Health Organization. Guidelines for the Treatment of Malaria. 3rd Edition. Geneva: World Health Organization, 2015.
WHO 2015c
-
- World Health Organization MPAC. Background document for Session 3 of the Malaria Policy Advisory Committee Meeting MPAC meeting, Sept 2015: Consensus modelling evidence to support the design of mass drug administration programs. www.who.int/malaria/mpac/mpac‐sept2015‐consensus‐modelling‐mda.pdf (accessed 16 January 2018).
WHO 2016
-
- World Health Organization. World Malaria Report 2016. www.who.int/malaria/publications/world‐malaria‐report‐2016/report/en/ (accessed 16 January 2018).
References to other published versions of this review
Graves 2012
Graves 2014
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

