H3 K27M-mutant gliomas in adults vs. children share similar histological features and adverse prognosis
- PMID: 29393845
- PMCID: PMC5822176
- DOI: 10.5414/NP301085
H3 K27M-mutant gliomas in adults vs. children share similar histological features and adverse prognosis
Abstract
Background: H3 K27M mutation was originally described in pediatric diffuse intrinsic pontine gliomas (DIPGs), but has been recently recognized to occur also in adult midline diffuse gliomas, as well as midline tumors with other morphologies, including gangliogliomas (GGs), anaplastic GGs, pilocytic astrocytomas (PAs), and posterior fossa ependymomas. In a few patients with H3 K27M;mutant tumors with these alternate morphologies, longer survival has been reported, making grading difficult for the neuropathologist. Few series compare tumors in adult vs. pediatric cohorts; we report our 4-year experience.
Materials and methods: Text Word database searches using H3 K27M in reports generated between January 2013 and November 10, 2017 were used to identify patients. Clinical and histological features as well as survival were evaluated for each case.
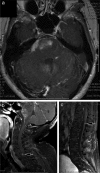
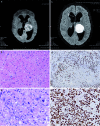
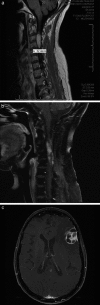
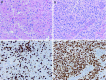
Results: 28 H3 K27M-mutant tumors were identified, with equal numbers of adults (13) vs. children (15). For adults, mean and median age was 52 years (range = 27 - 81 years), 2 decades older than a recently-published adult series. Tumors involved thalamic (adult = 7; pediatric = 7), spinal cord (adult = 4; pediatric = 2), pons (adult = 1; pediatric = 6), and hypothalamic (n = 1) sites. Other morphologies at presentation included pure GG (n = 3, pediatric) and PA (n = 1, adult). One adult and 1 pediatric patient each presented with leptomeningeal dissemination or developed leptomeningeal dissemination within 1 year after diagnosis, with transformation from PA or GG histology to glioblastoma. Mean survival was 9.3 (adults) vs. 8.9 (pediatric) months. Patients with tumors of other morphologies (GG, PA) did not enjoy extended survival.
Conclusion: H3 K27M-mutant tumors can affect patients at advanced ages, may show leptomeningeal dissemination at time of presentation, and "pure" GG or PA morphology is not rare. Regardless of patient age or tumor morphology, patients fare equally poorly. .
Figures
References
-
- Buczkowicz P Hoeman C Rakopoulos P Pajovic S Letourneau L Dzamba M Morrison A Lewis P Bouffet E Bartels U Zuccaro J Agnihotri S Ryall S Barszczyk M Chornenkyy Y Bourgey M Bourque G Montpetit A Cordero F Castelo-Branco P Genomic analysis of diffuse intrinsic pontine gliomas identifies three molecular subgroups and recurrent activating ACVR1 mutations. Nat Genet. 2014; 46: 451–456. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hawkins CED Sturm D Diffuse midline glioma, H3 K27M-mutant In: Louis D, Ohgaki, H, Wiestler, OD, Cavenee, WK, Ellison DW, Figarella-Branger, D, Perry, A, Reifenberger, G, von Deimling, A (ed). WHO classification of tumours of the central nervous system. 4th edn. Lyon, France: IARC; 2016. p. 57-59.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

