The journey of islet cell transplantation and future development
- PMID: 29394145
- PMCID: PMC5895174
- DOI: 10.1080/19382014.2018.1428511
The journey of islet cell transplantation and future development
Abstract
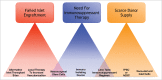
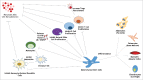
Intraportal islet transplantation has proven to be efficacious in preventing severe hypoglycemia and restoring insulin independence in selected patients with type 1 diabetes. Multiple islet infusions are often required to achieve and maintain insulin independence. Many challenges remain in clinical islet transplantation, including substantial islet cell loss early and late after islet infusion. Contributions to graft loss include the instant blood-mediated inflammatory reaction, potent host auto- and alloimmune responses, and beta cell toxicity from immunosuppressive agents. Protective strategies are being tested to circumvent several of these events including exploration of alternative transplantation sites, stem cell-derived insulin producing cell therapies, co-transplantation with mesenchymal stem cells or exploration of novel immune protective agents. Herein, we provide a brief introduction and history of islet cell transplantation, limitations associated with this procedure and methods to alleviate islet cell loss as a means to improve engraftment outcomes.
Keywords: immunosuppression; islet engraftment; islet transplantation; mesenchymal stem cells; pluripotent; type 1 diabetes; β cells.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells in the Curative Treatment of Diabetes and Potential Impediments Ahead.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2019;1144:25-35. doi: 10.1007/5584_2018_305. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2019. PMID: 30569414 Review.
-
Reduction of marginal mass required for successful islet transplantation in a diabetic rat model using adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stromal cells.Cytotherapy. 2018 Sep;20(9):1124-1142. doi: 10.1016/j.jcyt.2018.06.001. Epub 2018 Jul 29. Cytotherapy. 2018. PMID: 30068495
-
Evaluating Vascularization of Heterotopic Islet Constructs for Type 1 Diabetes Using an In Vitro Platform.Integr Biol (Camb). 2019 Nov 30;11(8):331-341. doi: 10.1093/intbio/zyz027. Integr Biol (Camb). 2019. PMID: 31724717
-
Stem-cell-based Therapies for Improving Islet Transplantation Outcomes in Type 1 Diabetes.Curr Diabetes Rev. 2018;14(1):3-13. doi: 10.2174/1573399812666160629094031. Curr Diabetes Rev. 2018. PMID: 27363412 Review.
-
Durable Control of Autoimmune Diabetes in Mice Achieved by Intraperitoneal Transplantation of "Neo-Islets," Three-Dimensional Aggregates of Allogeneic Islet and "Mesenchymal Stem Cells".Stem Cells Transl Med. 2017 Jul;6(7):1631-1643. doi: 10.1002/sctm.17-0005. Epub 2017 May 3. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2017. PMID: 28467694 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Current status of porcine islet xenotransplantation.Curr Opin Organ Transplant. 2020 Oct;25(5):449-456. doi: 10.1097/MOT.0000000000000794. Curr Opin Organ Transplant. 2020. PMID: 32773503 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Toward 3D-bioprinting of an endocrine pancreas: A building-block concept for bioartificial insulin-secreting tissue.J Tissue Eng. 2022 Apr 20;13:20417314221091033. doi: 10.1177/20417314221091033. eCollection 2022 Jan-Dec. J Tissue Eng. 2022. PMID: 35462988 Free PMC article.
-
RNA aptamers specific for transmembrane p24 trafficking protein 6 and Clusterin for the targeted delivery of imaging reagents and RNA therapeutics to human β cells.Nat Commun. 2022 Apr 5;13(1):1815. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-29377-3. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 35383192 Free PMC article.
-
Performance of islets of Langerhans conformally coated via an emulsion cross-linking method in diabetic rodents and nonhuman primates.Sci Adv. 2022 Jul;8(26):eabm3145. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abm3145. Epub 2022 Jun 29. Sci Adv. 2022. PMID: 35767620 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacologic adjunctive to insulin therapies in type 1 diabetes: The journey has just begun.World J Diabetes. 2019 Apr 15;10(4):234-240. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v10.i4.234. World J Diabetes. 2019. PMID: 31040899 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
