Regulating BMI1 expression via miRNAs promote Mesenchymal to Epithelial Transition (MET) and sensitizes breast cancer cell to chemotherapeutic drug
- PMID: 29394261
- PMCID: PMC5796693
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0190245
Regulating BMI1 expression via miRNAs promote Mesenchymal to Epithelial Transition (MET) and sensitizes breast cancer cell to chemotherapeutic drug
Abstract
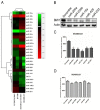
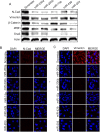
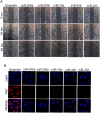
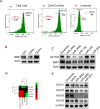
Polycomb group (PcG) proteinB lymphoma Mo-MLV insertion region 1 homolog (BMI1) is a transcriptional repressor that plays an important role in human carcinogenesis. MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are endogenous small non-coding RNAsthat implicate a negative regulation on gene expression. Deregulation of the expression of miRNAs has been implicated in tumorigenesis. Here, we have shown that knock-down ofBMI1increases theexpression of tumor-suppressivemiRNAs. Elevated levels of expression of miR-200a, miR-200b, miR-15a, miR-429, miR-203were observed upon knock-down of BMI1. Up-regulation of these miRNAsleads to down-regulation ofPRC1 group of proteins i.e. BMI1, RING1A, RING1B and Ub-H2A. Interestingly, overexpression of miR-200a, miR-200b and miR-15aalso produced decreased BMI1 and Ub-H2A protein expression in the CD44+ Cancer Stem Cellpopulation of MDAMB-231cells. Also,elevating the levels of BMI1 regulated miRNAspromoted Mesenchymal to Epithelial transition by regulating the expression of N-Cadherin, Vimentin, β-Catenin, Zeb, Snail thereby resulting in decreased invasion, migration and proliferation. Here, we also report that miR-200a, miR-200b, miR-203 accretes the sensitivity of MDAMB-231 cells to the histone deacetylase inhibitor (HDACi) SAHA and miR-15a sensitized breast cancer cells to the chemotherapeutic drug cisplatin leading to apoptosis. These findings suggest that modulatingspecific miRNAs may serve as a therapeutic approach for the treatment of breast cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
-
- Pietersen AM, Evers B, Prasad AA, Tanger E, Cornelissen-Steijger P, Jonkers J, et al. Bmi1 regulates stem cells and proliferation and differentiation of committed cells in mammary epithelium. Current biology: CB. 2008;18(14):1094–9. Epub 2008/07/19. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2008.06.070 . - DOI - PubMed
-
- Lukacs RU, Memarzadeh S, Wu H, Witte ON. Bmi-1 is a crucial regulator of prostate stem cell self-renewal and malignant transformation. Cell Stem Cell. 2010;7(6):682–93. Epub 2010/11/30. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2010.11.013 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ezhkova E, Pasolli HA, Parker JS, Stokes N, Su IH, Hannon G, et al. Ezh2 orchestrates gene expression for the stepwise differentiation of tissue-specific stem cells. Cell. 2009;136(6):1122–35. Epub 2009/03/24. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2008.12.043 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bracken AP, Pasini D, Capra M, Prosperini E, Colli E, Helin K. EZH2 is downstream of the pRB-E2F pathway, essential for proliferation and amplified in cancer. The EMBO journal. 2003;22(20):5323–35. Epub 2003/10/09. doi: 10.1093/emboj/cdg542 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Maynard MA, Ferretti R, Hilgendorf KI, Perret C, Whyte P, Lees JA. Bmi1 is required for tumorigenesis in a mouse model of intestinal cancer. Oncogene. 2014;33(28):3742–7. Epub 2013/08/21. doi: 10.1038/onc.2013.333 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

