Cortical and trabecular bone are equally affected in rats with renal failure and secondary hyperparathyroidism
- PMID: 29394885
- PMCID: PMC5796449
- DOI: 10.1186/s12882-018-0822-8
Cortical and trabecular bone are equally affected in rats with renal failure and secondary hyperparathyroidism
Abstract
Background: Changes in mineral metabolism and bone structure develop early in the course of chronic kidney disease and at end-stage are associated with increased risk of fragility fractures. The disruption of phosphorus homeostasis leads to secondary hyperparathyroidism, a common complication of chronic kidney disease. However, the molecular pathways by which high phosphorus influences bone metabolism in the early stages of the disease are not completely understood. We investigated the effects of a high phosphorus diet on bone and mineral metabolism using a 5/6 nephrectomy model of chronic kidney disease.
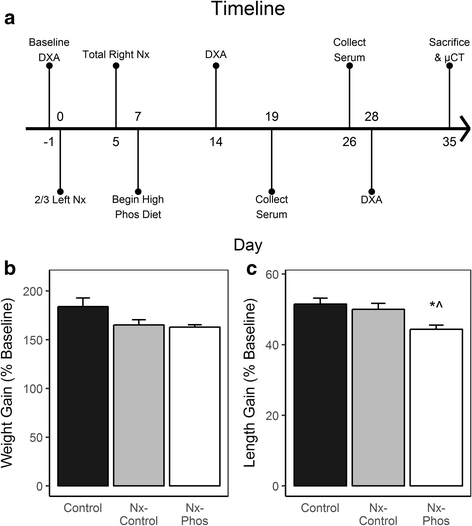
Methods: Four-week old rats were randomly assigned into groups: 1) Control with standard diet, 2) Nephrectomy with standard rodent diet, and 3) Nephrectomy with high phosphorus diet. Rats underwent in vivo imaging at baseline, day 14, and day 28, followed by ex vivo imaging.
Results: Cortical bone density at the femoral mid-diaphysis was reduced in nephrectomy-control and nephrectomy-high phosphorus compared to control rats. In contrast, trabecular bone mass was reduced at both the lumbar vertebrae and the femoral secondary spongiosa in nephrectomy-high phosphorus but not in nephrectomy-control. Reduced trabecular bone volume adjusted for tissue volume was caused by changes in trabecular number and separation at day 35. Histomorphometry revealed increased bone resorption in tibial secondary spongiosa in nephrectomy-control. High phosphorus diet-induced changes in bone microstructure were accompanied by increased serum parathyroid hormone and fibroblast growth factor 23 levels.
Conclusion: Our study demonstrates that changes in mineral metabolism and hormonal dysfunction contribute to trabecular and cortical bone changes in this model of early chronic kidney disease.
Keywords: Bone; Chronic kidney disease; FGF23; Phosphorus; Renal pathology.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval
Animal housing and procedures were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of the Jerry L. Pettis Memorial Veterans Affairs Medical Center. Rats were anesthetized with isoflurane prior to surgical procedures. All procedures performed complied with the principles and procedures of the Guidelines for the Care and Use of Experimental Animals.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures






References
-
- USRDS annual data report. Epidemiology of kidney disease in the United States. Bethesda, MD: National Institutes of Health, National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases; 2015.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

