Structural Connection between Activation Microswitch and Allosteric Sodium Site in GPCR Signaling
- PMID: 29395784
- PMCID: PMC5810373
- DOI: 10.1016/j.str.2017.12.013
Structural Connection between Activation Microswitch and Allosteric Sodium Site in GPCR Signaling
Abstract
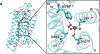
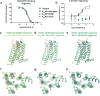
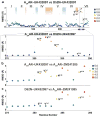
Sodium ions are endogenous allosteric modulators of many G-protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs). Mutation of key residues in the sodium binding motif causes a striking effect on G-protein signaling. We report the crystal structures of agonist complexes for two variants in the first sodium coordination shell of the human A2A adenosine receptor, D522.50N and S913.39A. Both structures present an overall active-like conformation; however, the variants show key changes in the activation motif NPxxY. Changes in the hydrogen bonding network in this microswitch suggest a possible mechanism for modified G-protein signaling and enhanced thermal stability. These structures, signaling data, and thermal stability analysis with a panel of pharmacological ligands provide a basis for understanding the role of the sodium-coordinating residues on stability and G-protein signaling. Utilizing the D2.50N variant is a promising method for stabilizing class A GPCRs to accelerate structural efforts and drug discovery.
Keywords: GPCR; adenosine receptor; allosteric modulators; cell signaling; crystallography; sodium binding; structural biology.
Copyright © 2018 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors have no conflicts of interests.
Figures
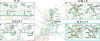
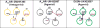
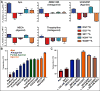

References
-
- Alexandrov AI, Mileni M, Chien EYT, Hanson MA, Stevens RC. Microscale Fluorescent Thermal Stability Assay for Membrane Proteins. Structure. 2008;16:351–359. - PubMed
-
- Ballesteros JA, Weinstein H. Integrated methods for the construction of three-dimensional models and computational probing of structure-function relations in G proteincoupled receptors. Methods Neurosci. 1995;25:366–428.
-
- Bonneau O, Wyss D, Ferretti S, Blaydon C, Stevenson CS, Trifilieff A. Effect of adenosine A2A receptor activation in murine models of respiratory disorders. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2006;290:L1036–1043. - PubMed
-
- Borroto-Escuela DO, Romero-Fernandez W, García-Negredo G, Correia PA, Garriga P, Fuxe K, Ciruela F. Dissecting the conserved NPxxY motif of the M3 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor: critical role of Asp-7.49 for receptor signaling and multiprotein complex formation. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2011;28:1009–1022. - PubMed
-
- Bouley R, Sun TX, Chenard M, McLaughlin M, McKee M, Lin HY, Brown D, Ausiello DA. Functional role of the NPxxY motif in internalization of the type 2 vasopressin receptor in LLC-PK1 cells. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2003;285:C750–C762. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

