A Subpopulation of Striatal Neurons Mediates Levodopa-Induced Dyskinesia
- PMID: 29398356
- PMCID: PMC6233726
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2018.01.017
A Subpopulation of Striatal Neurons Mediates Levodopa-Induced Dyskinesia
Abstract
Parkinson's disease is characterized by the progressive loss of midbrain dopamine neurons. Dopamine replacement therapy with levodopa alleviates parkinsonian motor symptoms but is complicated by the development of involuntary movements, termed levodopa-induced dyskinesia (LID). Aberrant activity in the striatum has been hypothesized to cause LID. Here, to establish a direct link between striatal activity and dyskinesia, we combine optogenetics and a method to manipulate dyskinesia-associated neurons, targeted recombination in active populations (TRAP). We find that TRAPed cells are a stable subset of sensorimotor striatal neurons, predominantly from the direct pathway, and that reactivation of TRAPed striatal neurons causes dyskinesia in the absence of levodopa. Inhibition of TRAPed cells, but not a nonspecific subset of direct pathway neurons, ameliorates LID. These results establish that a distinct subset of striatal neurons is causally involved in LID and indicate that successful therapeutic strategies for treating LID may require targeting functionally selective neuronal subtypes.
Keywords: Basal ganglia; Parkinson’s disease; direct pathway; dopamine; levodopa-induced dyskinesia; optogenetics.
Copyright © 2018 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
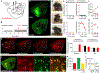

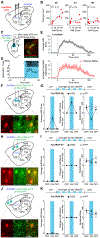
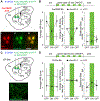
Comment in
-
Levodopa-Induced Dyskinesia: "TRAP"ping the Culprit.Mov Disord. 2018 May;33(5):761. doi: 10.1002/mds.27399. Epub 2018 May 3. Mov Disord. 2018. PMID: 29722458 No abstract available.
References
-
- Alam M, Rumpel R, Jin X, von Wrangel C, Tschirner SK, Krauss JK, Grothe C, Ratzka A, and Schwabe K (2017). Altered somatosensory cortex neuronal activity in a rat model of Parkinson’s disease and levodopa-induced dyskinesias. Exp. Neurol 294, 19–31. - PubMed
-
- Andersson M, Hilbertson A, and Cenci MA (1999). Striatal fosB expression is causally linked with l-DOPA-induced abnormal involuntary movements and the associated upregulation of striatal prodynorphin mRNA in a rat model of Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol. Dis 6, 461–474. - PubMed
-
- Bagetta V, Sgobio C, Pendolino V, Del Papa G, Tozzi A, Ghiglieri V, Giampà C, Zianni E, Gardoni F, Calabresi P, and Picconi B (2012). Rebalance of striatal NMDA/AMPA receptor ratio underlies the reduced emergence of dyskinesia during D2-like dopamine agonist treatment in experimental Parkinson’s disease. J. Neurosci 32, 17921–17931. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

