Pulmonary Comorbidity in Lung Cancer
- PMID: 29398402
- PMCID: PMC5937923
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molmed.2018.01.005
Pulmonary Comorbidity in Lung Cancer
Abstract
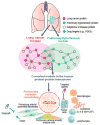
Pulmonary hypertension (PH) is caused by many disorders that affect the pulmonary vasculature. A recent study has provided evidence that pulmonary vascular remodeling and PH can be observed in lung cancer, and this may be associated with tumor cell-immune cell inflammatory crosstalk. These findings highlight the pressing need to understand better and manage pulmonary vascular comorbidities in lung cancer.
Keywords: cardio-oncology; disease comorbidity; inflammatory; lung cancer; pulmonary hypertension.
Copyright © 2018 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
Comment on
-
Lung cancer-associated pulmonary hypertension: Role of microenvironmental inflammation based on tumor cell-immune cell cross-talk.Sci Transl Med. 2017 Nov 15;9(416):eaai9048. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aai9048. Sci Transl Med. 2017. PMID: 29141888
References
-
- Siegel RL, et al. Cancer Statistics, 2017. CA Cancer J Clin. 2017;67:7–30. - PubMed
-
- Pullamsetti SS, et al. Lung cancer-associated pulmonary hypertension: role of microenvironmental inflammation based on tumor cell-immune cell crosstalk. Sci Transl Med. 2017;9:eaai9048. - PubMed
-
- Beuschlein F, et al. Somatic mutations in ATP1A1 and ATP2B3 lead to aldosterone-producing adenomas and secondary hypertension. Nat Genet. 2013;45:440–444. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

