Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury Reduces Long Term Renal Graft Survival: Mechanism and Beyond
- PMID: 29398595
- PMCID: PMC5835570
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2018.01.025
Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury Reduces Long Term Renal Graft Survival: Mechanism and Beyond
Abstract
Ischemia-reperfusion injury (IRI) during renal transplantation often initiates non-specific inflammatory responses that can result in the loss of kidney graft viability. However, the long-term consequence of IRI on renal grafts survival is uncertain. Here we review clinical evidence and laboratory studies, and elucidate the association between early IRI and later graft loss. Our critical analysis of previous publications indicates that early IRI does contribute to later graft loss through reduction of renal functional mass, graft vascular injury, and chronic hypoxia, as well as subsequent fibrosis. IRI is also known to induce kidney allograft dysfunction and acute rejection, reducing graft survival. Therefore, attempts have been made to substitute traditional preserving solutions with novel agents, yielding promising results.
Keywords: Acute rejection; Graft survival; Ischemia-reperfusion; Renal transplantation; Th cells: T helper cells.
Copyright © 2018 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
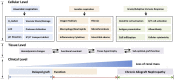
Figures


References
-
- Amin R., Turner C., van Aken S., Bahu T.K., Watts A., Lindsell D.R., Dalton R.N., Dunger D.B. The relationship between microalbuminuria and glomerular filtration rate in young type 1 diabetic subjects: the Oxford Regional Prospective Study. Kidney Int. 2005;68:1740–1749. - PubMed
-
- Barba J., Zudaire J.J., Robles J.E., Tienza A., Rosell D., Berian J.M., Pascual I. Is there a safe cold ischemia time interval for the renal graft? Actas Urol. Esp. 2011;35:475–480. - PubMed
-
- Basile D.P., Donohoe D., Roethe K., Osborn J.L. Renal ischemic injury results in permanent damage to peritubular capillaries and influences long-term function. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 2001;281:F887–99. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

