Allergic Conjunctivitis-induced Retinal Inflammation Promotes Myopia Progression
- PMID: 29398596
- PMCID: PMC5835569
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2018.01.024
Allergic Conjunctivitis-induced Retinal Inflammation Promotes Myopia Progression
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum to "Allergic Conjunctivitis-induced Retinal Inflammation Promotes Myopia Progression" [EBioMedicine 28 (2018) 274-286].EBioMedicine. 2019 Mar;41:717-718. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2019.02.046. Epub 2019 Mar 16. EBioMedicine. 2019. PMID: 30885727 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
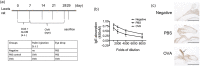
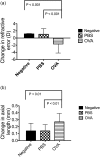
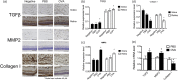
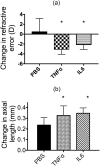
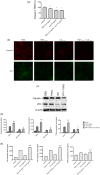
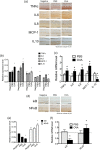
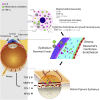
Myopia is a highly prevalent eye disease. There is limited information suggesting a relationship between myopia and inflammation. We found children with allergic conjunctivitis (AC) had the highest adjusted odds ratio (1.75, 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.72-1.77) for myopia among the four allergic diseases. A cohort study was conducted and confirmed that children with AC had a higher incidence and subsequent risk of myopia (hazard ratio 2.35, 95%CI 2.29-2.40) compared to those without AC. Lower refractive error and longer axial length were observed in an AC animal model. Myopia progression was enhanced by tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α or interleukin (IL)-6 administration, two cytokines secreted by mast cell degranulation. The TNF-α or IL-6 weakened the tight junction formed by corneal epithelial (CEP) cells and inflammatory cytokines across the layer of CEP cells, which increased the levels of TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-8 secreted by retinal pigment epithelial cells. The expression levels of TNF-α, IL-6, IL-8, monocyte chemoattractant protein-1, and nuclear factor kappa B were up-regulated in eyes with AC, whereas IL-10 and the inhibitor of kappa B were down-regulated. In conclusion, the experimental findings in mice corroborate the epidemiological data showing that allergic inflammation influences the development of myopia.
Keywords: Allergic conjunctivitis; Allergic rhinitis; Asthma; Atopic dermatitis; Inflammation; Myopia; Population-based study.
Copyright © 2018. Published by Elsevier B.V.
Figures

References
-
- Abraham E., Arcaroli J., Shenkar R. Activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinases, NF-kappa B, and cyclic adenosine 5′-monophosphate response element-binding protein in lung neutrophils occurs by differing mechanisms after hemorrhage or endotoxemia. J. Immunol. 2001;166(1):522–530. - PubMed
-
- Akasu T., Tsurusaki M. Interleukin-1beta causes a biphasic response in neurons of rat major pelvic ganglia. Neurosci. Lett. 1999;272(2):119–122. - PubMed
-
- Bacic F., Uematsu S., McCarron R.M., Spatz M. Dopaminergic receptors linked to adenylate cyclase in human cerebromicrovascular endothelium. J. Neurochem. 1991;57(5):1774–1780. - PubMed
-
- Basu S., Dasgupta P.S. Dopamine, a neurotransmitter, influences the immune system. J. Neuroimmunol. 2000;102(2):113–124. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

