The effect of hydroxy safflower yellow A on coronary heart disease through Bcl-2/Bax and PPAR-γ
- PMID: 29399062
- PMCID: PMC5769294
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2017.5414
The effect of hydroxy safflower yellow A on coronary heart disease through Bcl-2/Bax and PPAR-γ
Abstract
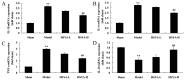
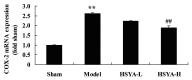
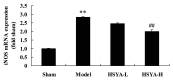
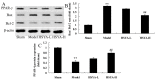
The aim of the present study was to investigate the effect of hydroxy safflower yellow A (HSYA) on coronary heart disease through assessing the expression of B-cell lymphoma 2 (Bcl-2)/Bcl-2-like protein 4 (Bax) and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR)-γ. Coronary heart disease was induced in male Bama miniature swines via thoracoscope to serve as an animal model. Coronary heart disease swine were lavaged with 20 or 40 mg/kg HSYA. The mRNA levels of tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α, interleukin (IL)-1β, IL-6, IL-10, cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) and inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) were detected using reverse transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction. The protein expression of Bcl-2, Bax, PPAR-γ, phosphorylation of Janus kinase (JAK)2 and phosphorylation of signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT)3 were detected using western blot analysis. Treatment with HSYA significantly suppressed the mRNA levels of IL-1β (P<0.01), IL-6 (P<0.01), TNF-α (P<0.01), COX-2 (P<0.01) and iNOS (P<0.01), and significantly increased IL-10 mRNA level in the coronary heart disease model (P<0.01). Furthermore, HSYA treatment significantly decreased the Bcl-2/Bax ratio (P<0.01) in the coronary heart disease model group, and enhanced the phosphorylation of JAK2/STAT3 pathway (P<0.01). However, HSYA had no significant effect on the expression of PPAR-γ protein. The results of the present study suggest that HSYA is able to weaken coronary heart disease via inflammation, Bcl-2/Bax and the PPAR-γ signaling pathway.
Keywords: B-cell lymphoma 2; B-cell lymphoma-like protein 4; coronary heart disease; hydroxy safflower yellow A; inflammation; peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ.
Figures

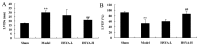


References
-
- Berndt N, Bolman C, Froelicher ES, Mudde A, Candel M, de Vries H, Lechner L. Effectiveness of a telephone delivered and a face-to-face delivered counseling intervention for smoking cessation in patients with coronary heart disease: A 6-month follow-up. J Behav Med. 2014;37:709–724. - PubMed
-
- Moser DK, McKinley S, Riegel B, Doering LV, Meischke H, Pelter M, Davidson P, Baker H, Dracup K. The impact on anxiety and perceived control of a short one-on-one nursing intervention designed to decrease treatment seeking delay in people with coronary heart disease. Eur J Cardiovasc Nurs. 2012;11:160–167. doi: 10.1016/j.ejcnurse.2010.11.003. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Grunwald V, Karakiewicz PI, Bavbek SE, Miller K, Machiels JP, Lee SH, Larkin J, Bono P, Rha SY, Castellano D, et al. An international expanded-access programme of everolimus: Addressing safety and efficacy in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma who progress after initial vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-tyrosine kinase inhibitor therapy. Eur J Cancer. 2012;48:324–332. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2011.06.054. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Derosa G, Bonaventura A, Bianchi L, Romano D, D'Angelo A, Fogari E, Maffioli P. A randomized, placebo-controlled study on the effects of a nutraceutical combination of red yeast rice, silybum marianum and octasonol on lipid profile, endothelial and inflammatory parameters. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents. 2014;28:317–324. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
