Effects of telmisartan on vascular endothelial function, inflammation and insulin resistance in patients with coronary heart disease and diabetes mellitus
- PMID: 29399098
- PMCID: PMC5772733
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2017.5451
Effects of telmisartan on vascular endothelial function, inflammation and insulin resistance in patients with coronary heart disease and diabetes mellitus
Abstract
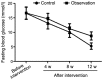
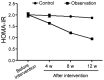
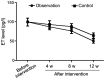
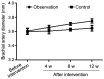
The aim of the present study was to investigate the effects of telmisartan on vascular endothelial functions, inflammatory factors and insulin resistance of coronary heart disease patients complicated with diabetes mellitus. In total, 80 coronary heart disease patients complicated with type 2 diabetes mellitus, admitted and treated in the Zhangqiu Hospital from January 2016 to March 2017 were enrolled in the study. Each patient was randomly assigned to an observation (n=40) or a control group (n=40) using a random number table. Conventional symptomatic and supporting therapies were administered to all the patients in the two groups for 12 consecutive weeks, while additional telmisartan was given only to patients in the observation group. Markers of glucose metabolism, vascular endothelial function and inflammation were determined before and after intervention, to compare averages between groups. Results showed the levels of fasting blood glucose and blood glucose in the observation group were significantly lower than those in the control group (p<0.05) after 4 weeks of treatment. The levels of HOMA-IR in the observation group were clearly improved compared to those in the control group during the same period (p<0.05). After the intervention, the levels of FINS and HOMA-IR in the observation group improved significantly more compared with those in the control group (p<0.05), while the levels of tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), interleukin-6 (IL-6) and C-reactive protein (CRP) were much lower than those in the control group (p<0.05). Furthermore, at the 4th, 8th and 12th week after starting the treatment, the vascular endothelin (ET) levels in the observation group were significantly lower than those in the control group (p<0.05). In addition, the brachial artery diameters in the basal state were significantly larger than those in the control group (p<0.05) for the same time-points. Coronary heart disease patients complicated with diabetes mellitus whose treatment includes telmisartan can better regulate their blood glucose, reduce the insulin resistance and body inflammatory responses and improve their vascular endothelial functions.
Keywords: coronary heart disease; diabetes mellitus; inflammatory factor; insulin resistance; telmisartan; vascular endothelial function.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effect of rosuvastatin on vascular endothelial functions and inflammatory factors of patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and coronary heart disease.Exp Ther Med. 2019 Jan;17(1):332-336. doi: 10.3892/etm.2018.6923. Epub 2018 Nov 2. Exp Ther Med. 2019. PMID: 30651799 Free PMC article.
-
A study of the correlation of insulin resistance and leptin with inflammatory factors and vascular endothelial injury in T2DM patients with CHD.Exp Ther Med. 2018 Jul;16(1):265-269. doi: 10.3892/etm.2018.6170. Epub 2018 May 16. Exp Ther Med. 2018. PMID: 29896248 Free PMC article.
-
Insulin resistance, blood glucose and inflammatory cytokine levels are risk factors for cardiovascular events in diabetic patients complicated with coronary heart disease.Exp Ther Med. 2018 Feb;15(2):1515-1519. doi: 10.3892/etm.2017.5584. Epub 2017 Nov 30. Exp Ther Med. 2018. PMID: 29434736 Free PMC article.
-
The relationship between insulin resistance, adiponectin and C-reactive protein and vascular endothelial injury in diabetic patients with coronary heart disease.Exp Ther Med. 2018 Sep;16(3):2022-2026. doi: 10.3892/etm.2018.6407. Epub 2018 Jul 4. Exp Ther Med. 2018. PMID: 30186434 Free PMC article.
-
Potential biomarkers of insulin resistance and atherosclerosis in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients with coronary artery disease.Int J Endocrinol. 2013;2013:698567. doi: 10.1155/2013/698567. Epub 2013 Oct 24. Int J Endocrinol. 2013. PMID: 24282409 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Telmisartan mitigates lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced production of mucin 5AC (MUC5AC) through increasing suppressor of cytokine signaling 1 (SOCS1).Bioengineered. 2021 Dec;12(1):3912-3923. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2021.1943605. Bioengineered. 2021. PMID: 34281463 Free PMC article.
-
The time dimension to stroke: Circadian effects on stroke outcomes and mechanisms.Neurochem Int. 2023 Jan;162:105457. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2022.105457. Epub 2022 Nov 25. Neurochem Int. 2023. PMID: 36442686 Free PMC article.
-
Telmisartan is neuroprotective in a hiPSC-derived spinal microtissue model for C9orf72 ALS via inhibition of neuroinflammation.Stem Cell Reports. 2025 Jul 8;20(7):102535. doi: 10.1016/j.stemcr.2025.102535. Epub 2025 Jun 19. Stem Cell Reports. 2025. PMID: 40541176 Free PMC article.
-
Telmisartan Loaded Nanofibers Enhance Re-Endothelialization and Inhibit Neointimal Hyperplasia.Pharmaceutics. 2021 Oct 21;13(11):1756. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics13111756. Pharmaceutics. 2021. PMID: 34834171 Free PMC article.
-
ChaiQi Decoction Alleviates Vascular Endothelial Injury by Downregulating the Inflammatory Response in ApoE-Model Mice.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021 Feb 10;2021:9415819. doi: 10.1155/2021/9415819. eCollection 2021. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021. PMID: 33628325 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Park S, Kario K, Park CG, Huang QF, Cheng HM, Hoshide S, Wang JG, Chen CH, Characteristics On the ManagEment of Hypertension in Asia-Morning Hypertension Discussion Group (COME Asia MHDG) Target blood pressure in patients with diabetes: Asian perspective. Yonsei Med J. 2016;57:1307–1311. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2016.57.6.1307. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bays H, Gao P, Völker B, Mattheus M, Ruilope LM, Zhu D. Efficacy of single-pill combination of telmisartan 80 mg and hydrochlorothiazide 25 mg in patients with cardiovascular disease risk factors: A prospective subgroup analysis of a randomized, double-blind, and controlled trial. Int J Hypertens. 2013;2013:749830. doi: 10.1155/2013/749830. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Verdecchia P, Dagenais G, Healey J, Gao P, Dans AL, Chazova I, Binbrek AS, Iacobellis G, Ferreira R, Holwerda N, et al. Ongoing Telmisartan Alone and in Combination With Ramipril Global Endpoint TrialTelmisartan Randomized AssessmeNt Study in ACE iNtolerant subjects with cardiovascular Disease Investigators Blood pressure and other determinants of new-onset atrial fibrillation in patients at high cardiovascular risk in the Ongoing Telmisartan Alone and in Combination With Ramipril Global Endpoint Trial/Telmisartan Randomized Assessment Study in ACE intolerant subjects with cardiovascular Disease studies. J Hypertens. 2012;30:1004–1014. doi: 10.1097/HJH.0b013e3283522a51. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
