Role of inflammatory response in liver diseases: Therapeutic strategies
- PMID: 29399273
- PMCID: PMC5787673
- DOI: 10.4254/wjh.v10.i1.1
Role of inflammatory response in liver diseases: Therapeutic strategies
Abstract
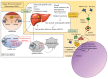
Inflammation and tumorigenesis are tightly linked pathways impacting cancer development. Inflammasomes are key signalling platforms that detect pathogenic microorganisms, including hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection, and sterile stressors (oxidative stress, insulin resistance, lipotoxicity) able to activate pro-inflammatory cytokines interleukin-1β and IL-18. Most of the inflammasome complexes that have been described to date contain a NOD-like receptor sensor molecule. Redox state and autophagy can regulate inflammasome complex and, depending on the conditions, can be either pro- or anti-apoptotic. Acute and chronic liver diseases are cytokine-driven diseases as several proinflammatory cytokines (IL-1α, IL-1β, tumor necrosis factor-alpha, and IL-6) are critically involved in inflammation, steatosis, fibrosis, and cancer development. NLRP3 inflammasome gain of function aggravates liver disease, resulting in severe liver fibrosis and highlighting this pathway in the pathogenesis of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. On the other hand, HCV infection is the primary catalyst for progressive liver disease and development of liver cancer. It is well established that HCV-induced IL-1β production by hepatic macrophages plays a critical and central process that promotes liver inflammation and disease. In this review, we aim to clarify the role of the inflammasome in the aggravation of liver disease, and how selective blockade of this main pathway may be a useful strategy to delay fibrosis progression in liver diseases.
Keywords: Caspase-1; Fibrosis; Hepatitis C virus; Inflammasome; Interleukin-1α; Interleukin-1β; Liver disease; NLRP3; Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease; Tumor necrosis factor-alpha.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: Authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Younossi ZM, Loomba R, Anstee QM, Rinella ME, Bugianesi E, Marchesini G, Neuschwander-Tetri BA, Serfaty L, Negro F, Caldwell SH, et al. Diagnostic Modalities for Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD), Non-alcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH) and Associated Fibrosis. Hepatology. 2017 Epub ahead of print. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ludwig J, Viggiano TR, McGill DB, Oh BJ. Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: Mayo Clinic experiences with a hitherto unnamed disease. Mayo Clin Proc. 1980;55:434–438. - PubMed
-
- Chalasani N, Younossi Z, Lavine JE, Diehl AM, Brunt EM, Cusi K, Charlton M, Sanyal AJ. The diagnosis and management of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: practice Guideline by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases, American College of Gastroenterology, and the American Gastroenterological Association. Hepatology. 2012;55:2005–2023. - PubMed
-
- Loomba R, Sanyal AJ. The global NAFLD epidemic. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013;10:686–690. - PubMed
-
- Buzzetti E, Pinzani M, Tsochatzis EA. The multiple-hit pathogenesis of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) Metabolism. 2016;65:1038–1048. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

