DNA methylation as a mediator of the association between prenatal adversity and risk factors for metabolic disease in adulthood
- PMID: 29399631
- PMCID: PMC5792223
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.aao4364
DNA methylation as a mediator of the association between prenatal adversity and risk factors for metabolic disease in adulthood
Abstract
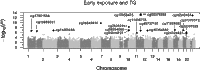
Although it is assumed that epigenetic mechanisms, such as changes in DNA methylation (DNAm), underlie the relationship between adverse intrauterine conditions and adult metabolic health, evidence from human studies remains scarce. Therefore, we evaluated whether DNAm in whole blood mediated the association between prenatal famine exposure and metabolic health in 422 individuals exposed to famine in utero and 463 (sibling) controls. We implemented a two-step analysis, namely, a genome-wide exploration across 342,596 cytosine-phosphate-guanine dinucleotides (CpGs) for potential mediators of the association between prenatal famine exposure and adult body mass index (BMI), serum triglycerides (TG), or glucose concentrations, which was followed by formal mediation analysis. DNAm mediated the association of prenatal famine exposure with adult BMI and TG but not with glucose. DNAm at PIM3 (cg09349128), a gene involved in energy metabolism, mediated 13.4% [95% confidence interval (CI), 5 to 28%] of the association between famine exposure and BMI. DNAm at six CpGs, including TXNIP (cg19693031), influencing β cell function, and ABCG1 (cg07397296), affecting lipid metabolism, together mediated 80% (95% CI, 38.5 to 100%) of the association between famine exposure and TG. Analyses restricted to those exposed to famine during early gestation identified additional CpGs mediating the relationship with TG near PFKFB3 (glycolysis) and METTL8 (adipogenesis). DNAm at the CpGs involved was associated with gene expression in an external data set and correlated with DNAm levels in fat depots in additional postmortem data. Our data are consistent with the hypothesis that epigenetic mechanisms mediate the influence of transient adverse environmental factors in early life on long-term metabolic health. The specific mechanism awaits elucidation.
Figures

References
-
- D. J. P. Barker, Fetal and Infant Origins of Adult Disease (British Medical Journal, 1992). - PubMed
-
- Waterland R. A., Michels K. B., Epigenetic epidemiology of the developmental origins hypothesis. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 27, 363–388 (2007). - PubMed
-
- Jaenisch R., Bird A., Epigenetic regulation of gene expression: How the genome integrates intrinsic and environmental signals. Nat. Genet. 33, 245–254 (2003). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

