Spatially resolved RNA-sequencing of the embryonic heart identifies a role for Wnt/β-catenin signaling in autonomic control of heart rate
- PMID: 29400650
- PMCID: PMC5815850
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.31515
Spatially resolved RNA-sequencing of the embryonic heart identifies a role for Wnt/β-catenin signaling in autonomic control of heart rate
Abstract
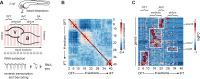
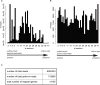
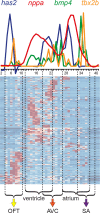
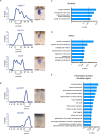
Development of specialized cells and structures in the heart is regulated by spatially -restricted molecular pathways. Disruptions in these pathways can cause severe congenital cardiac malformations or functional defects. To better understand these pathways and how they regulate cardiac development we used tomo-seq, combining high-throughput RNA-sequencing with tissue-sectioning, to establish a genome-wide expression dataset with high spatial resolution for the developing zebrafish heart. Analysis of the dataset revealed over 1100 genes differentially expressed in sub-compartments. Pacemaker cells in the sinoatrial region induce heart contractions, but little is known about the mechanisms underlying their development. Using our transcriptome map, we identified spatially restricted Wnt/β-catenin signaling activity in pacemaker cells, which was controlled by Islet-1 activity. Moreover, Wnt/β-catenin signaling controls heart rate by regulating pacemaker cellular response to parasympathetic stimuli. Thus, this high-resolution transcriptome map incorporating all cell types in the embryonic heart can expose spatially restricted molecular pathways critical for specific cardiac functions.
Keywords: Islet-1; RNA-seq; developmental biology; heart; pacemaker; stem cells; wnt; zebrafish.
© 2018, Burkhard et al.
Conflict of interest statement
SB, JB No competing interests declared
Figures



Similar articles
-
Crosstalk between AhR and wnt/β-catenin signal pathways in the cardiac developmental toxicity of PM2.5 in zebrafish embryos.Toxicology. 2016 Apr 29;355-356:31-8. doi: 10.1016/j.tox.2016.05.014. Epub 2016 May 20. Toxicology. 2016. PMID: 27216425
-
Biphasic role for Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in cardiac specification in zebrafish and embryonic stem cells.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007 Jun 5;104(23):9685-90. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0702859104. Epub 2007 May 23. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007. PMID: 17522258 Free PMC article.
-
Distinct functions of Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in KV development and cardiac asymmetry.Development. 2009 Jan;136(2):207-17. doi: 10.1242/dev.029561. Development. 2009. PMID: 19103803
-
Wnt/beta-catenin signaling and cardiogenesis: timing does matter.Dev Cell. 2007 Jul;13(1):10-3. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2007.06.006. Dev Cell. 2007. PMID: 17609106 Review.
-
Cell-cell interaction in the heart via Wnt/β-catenin pathway after cardiac injury.Cardiovasc Res. 2014 May 1;102(2):214-23. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvu054. Epub 2014 Mar 3. Cardiovasc Res. 2014. PMID: 24591151 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Single-cell profiling of the developing embryonic heart in Drosophila.Development. 2023 Aug 15;150(16):dev201936. doi: 10.1242/dev.201936. Epub 2023 Aug 24. Development. 2023. PMID: 37526610 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of astroglia-like cardiac nexus glia that are critical regulators of cardiac development and function.PLoS Biol. 2021 Nov 18;19(11):e3001444. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3001444. eCollection 2021 Nov. PLoS Biol. 2021. PMID: 34793438 Free PMC article.
-
On Zebrafish Disease Models and Matters of the Heart.Biomedicines. 2019 Feb 28;7(1):15. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines7010015. Biomedicines. 2019. PMID: 30823496 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The pericardium forms as a distinct structure during heart formation.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Sep 28:2024.09.18.613484. doi: 10.1101/2024.09.18.613484. bioRxiv. 2024. PMID: 39345600 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Cfdp1 Is Essential for Cardiac Development and Function.Cells. 2023 Aug 3;12(15):1994. doi: 10.3390/cells12151994. Cells. 2023. PMID: 37566073 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Beis D, Bartman T, Jin SW, Scott IC, D'Amico LA, Ober EA, Verkade H, Frantsve J, Field HA, Wehman A, Baier H, Tallafuss A, Bally-Cuif L, Chen JN, Stainier DY, Jungblut B. Genetic and cellular analyses of zebrafish atrioventricular cushion and valve development. Development. 2005;132:4193–4204. doi: 10.1242/dev.01970. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

