Lipids Alter Rhodopsin Function via Ligand-like and Solvent-like Interactions
- PMID: 29401433
- PMCID: PMC5984976
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bpj.2017.11.021
Lipids Alter Rhodopsin Function via Ligand-like and Solvent-like Interactions
Abstract
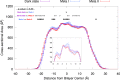
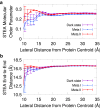
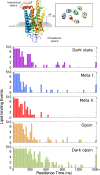
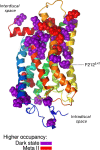
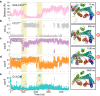
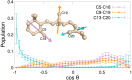
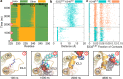
Rhodopsin, a prototypical G protein-coupled receptor, is a membrane protein that can sense dim light. This highly effective photoreceptor is known to be sensitive to the composition of its lipidic environment, but the molecular mechanisms underlying this fine-tuned modulation of the receptor's function and structural stability are not fully understood. There are two competing hypotheses to explain how this occurs: 1) lipid modulation occurs via solvent-like interactions, where lipid composition controls membrane properties like hydrophobic thickness, which in turn modulate the protein's conformational equilibrium; or 2) protein-lipid interactions are ligand-like, with specific hot spots and long-lived binding events. By analyzing an ensemble of all-atom molecular dynamics simulations of five different states of rhodopsin, we show that a local ordering effect takes place in the membrane upon receptor activation. Likewise, docosahexaenoic acid acyl tails and phosphatidylethanolamine headgroups behave like weak ligands, preferentially binding to the receptor in inactive-like conformations and inducing subtle but significant structural changes.
Copyright © 2017 Biophysical Society. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Palsdottir H., Hunte C. Lipids in membrane protein structures. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2004;1666:2–18. - PubMed
-
- Vigh L., Escribá P.V., Harwood J.L. The significance of lipid composition for membrane activity: new concepts and ways of assessing function. Prog. Lipid Res. 2005;44:303–344. - PubMed
-
- Gibson N.J., Brown M.F. Lipid headgroup and acyl chain composition modulate the MI-MII equilibrium of rhodopsin in recombinant membranes. Biochemistry. 1993;32:2438–2454. - PubMed
-
- Litman B.J., Mitchell D.C. A role for phospholipid polyunsaturation in modulating membrane protein function. Lipids. 1996;31:S193–S197. - PubMed
-
- Hashimoto M., Hossain M.S., Shido O. Effects of docosahexaenoic acid on annular lipid fluidity of the rat bile canalicular plasma membrane. J. Lipid Res. 2001;42:1160–1168. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

