Inflammatory markers, the tryptophan-kynurenine pathway, and vitamin B status after bariatric surgery
- PMID: 29401505
- PMCID: PMC5798786
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0192169
Inflammatory markers, the tryptophan-kynurenine pathway, and vitamin B status after bariatric surgery
Abstract
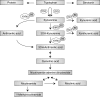
Objective: Obesity is associated with increased inflammation and insulin resistance. In conditions with chronic immune activation, low plasma vitamin B6-levels are described, as well as an increased kynurenine:tryptophan-ratio (KTR). We investigated circulating tryptophan, kynurenine and its metabolites, neopterin, B-vitamins, CRP, and HbA1c in individuals with obesity before and after bariatric surgery.
Methods: This longitudinal study included 37 patients with severe obesity, scheduled for bariatric surgery. Blood samples were taken at inclusion and at three months and one year postoperatively.
Results: We observed significant positive correlations between HbA1c and both 3-hydroxy-kynurenine and 3-hydroxyanthranilic acid at inclusion. After surgery, fasting glucose, HbA1C and triglycerides decreased, whereas HDL-cholesterol increased. Tryptophan, kynurenine and its metabolites, except for anthranilic acid, decreased during weight loss. The KTR and CRP decreased while vitamin B6 increased during the year following operation, indicating reduced inflammation (all p<0.05).
Conclusions: In patients with obesity subjected to bariatric surgery, levels of 3-hydroxykynurenine and 3-hydroxyanthranilic acid seemed to be positively correlated to impaired glucose tolerance. One year following surgery, plasma levels of the kynurenine metabolites were substantially decreased, along with a metabolic improvement. The relation of circulating kynurenine pathway metabolites with biomarkers of metabolic impairment in patients with obesity needs further evaluation.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Finucane MM, Stevens GA, Cowan MJ, Danaei G, Lin JK, Paciorek CJ, et al. National, regional, and global trends in body-mass index since 1980: systematic analysis of health examination surveys and epidemiological studies with 960 country-years and 9.1 million participants. Lancet. 2011;377(9765):557–67. Epub 2011/02/08. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(10)62037-5 . - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Prospective Studies C, Whitlock G, Lewington S, Sherliker P, Clarke R, Emberson J, et al. Body-mass index and cause-specific mortality in 900 000 adults: collaborative analyses of 57 prospective studies. Lancet. 2009;373(9669):1083–96. Epub 2009/03/21. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(09)60318-4 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC2662372. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Sjostrom L, Peltonen M, Jacobson P, Ahlin S, Andersson-Assarsson J, Anveden A, et al. Association of bariatric surgery with long-term remission of type 2 diabetes and with microvascular and macrovascular complications. JAMA. 2014;311(22):2297–304. Epub 2014/06/11. doi: 10.1001/jama.2014.5988 . - DOI - PubMed
-
- Gloy VL, Briel M, Bhatt DL, Kashyap SR, Schauer PR, Mingrone G, et al. Bariatric surgery versus non-surgical treatment for obesity: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. BMJ. 2013;347:f5934 Epub 2013/10/24. doi: 10.1136/bmj.f5934 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC3806364. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Grant RW, Stephens JM. Fat in flames: Influence of cytokines and pattern recognition receptors on adipocyte lipolysis. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2015:ajpendo 00053 2015. Epub 2015/06/11. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00053.2015 . - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

