Differential susceptibility of Dectin-1 isoforms to functional inactivation by neutrophil and fungal proteases
- PMID: 29401615
- PMCID: PMC5956239
- DOI: 10.1096/fj.201701145R
Differential susceptibility of Dectin-1 isoforms to functional inactivation by neutrophil and fungal proteases
Abstract
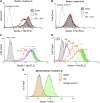
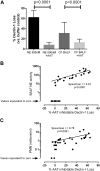
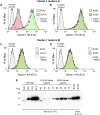
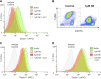
Patients with cystic fibrosis (CF) experience chronic or recurrent bacterial and fungal lung infections. Many patients with CF cannot effectively clear Aspergillus from their lungs. This may result in IgE sensitization and the development of allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis, or invasive infections, such as Aspergillus bronchitis. Lung disease in patients with CF is associated with neutrophil-dominated inflammation and elevated levels of the serine protease, neutrophil elastase (NE). Various C-type lectin-like receptors (CLRs), including Dectin-1 and Dectin-2, are involved in the immune response to Aspergillus. Here, we show that purified NE cleaves Dectin-1 in an isoform-specific manner. Bronchoalveolar lavage fluid from patients with CF, which contains high NE activity, induces Dectin-1 cleavage. Similarly, filtrate from a protease-producing strain of Aspergillus fumigatus induces isoform-specific cleavage of Dectin-1. Dectin-1 knockout (KO) cells and NE-treated cells demonstrated reduced phagocytosis of zymosan, a fungal cell wall preparation. In addition, NE cleaves 2 other CLRs, Dectin-2 and Mincle, and fungal-induced cytokine production was reduced in Dectin-1 KO cells, Dectin-2 KO cells, and NE-treated cells. Thus, Dectin-1 and Dectin-2 cleavage by NE and/or A. fumigatus-derived proteases results in an aberrant antifungal immune response that likely contributes to disease pathology in patients with CF.-Griffiths, J. S., Thompson, A., Stott, M., Benny, A., Lewis, N. A., Taylor, P. R., Forton, J., Herrick, S., Orr, S. J., McGreal, E. P. Differential susceptibility of Dectin-1 isoforms to functional inactivation by neutrophil and fungal proteases.
Keywords: Aspergillus; C-type lectin-like receptor; cystic fibrosis; elastase.
Figures


References
-
- Brown G. D., Denning D. W., Gow N. A., Levitz S. M., Netea M. G., White T. C. (2012) Hidden killers: human fungal infections. Sci. Transl. Med. 4, 165rv13 - PubMed
-
- King J., Brunel S. F., Warris A. (2016) Aspergillus infections in cystic fibrosis. J. Infect. 72(Suppl), S50–S55 - PubMed
-
- El-Dahr J. M., Fink R., Selden R., Arruda L. K., Platts-Mills T. A., Heymann P. W. (1994) Development of immune responses to Aspergillus at an early age in children with cystic fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 150, 1513–1518 - PubMed
-
- Baxter C. G., Dunn G., Jones A. M., Webb K., Gore R., Richardson M. D., Denning D. W. (2013) Novel immunologic classification of aspergillosis in adult cystic fibrosis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 132, 560–566.e510 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

