CoVaCS: a consensus variant calling system
- PMID: 29402227
- PMCID: PMC5800023
- DOI: 10.1186/s12864-018-4508-1
CoVaCS: a consensus variant calling system
Abstract
Background: The advent and ongoing development of next generation sequencing technologies (NGS) has led to a rapid increase in the rate of human genome re-sequencing data, paving the way for personalized genomics and precision medicine. The body of genome resequencing data is progressively increasing underlining the need for accurate and time-effective bioinformatics systems for genotyping - a crucial prerequisite for identification of candidate causal mutations in diagnostic screens.
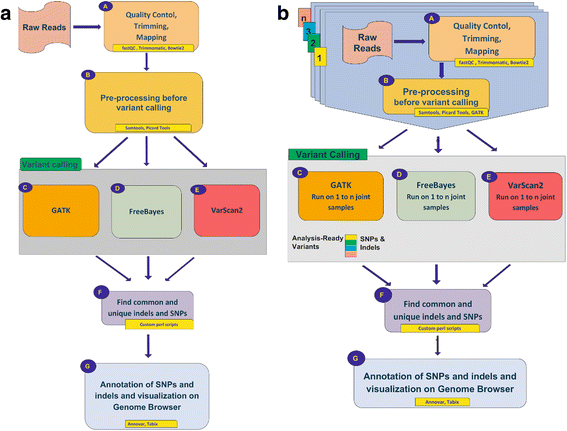
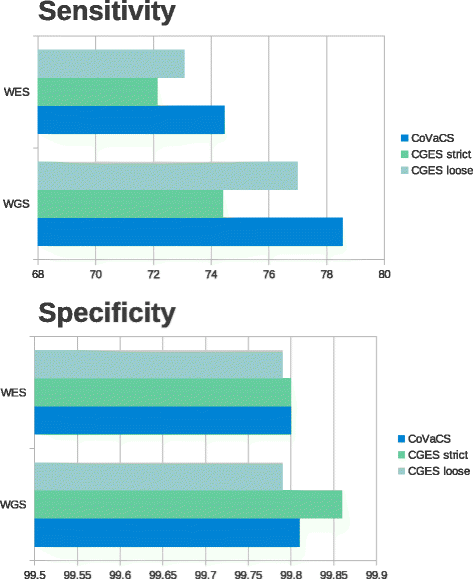
Results: Here we present CoVaCS, a fully automated, highly accurate system with a web based graphical interface for genotyping and variant annotation. Extensive tests on a gold standard benchmark data-set -the NA12878 Illumina platinum genome- confirm that call-sets based on our consensus strategy are completely in line with those attained by similar command line based approaches, and far more accurate than call-sets from any individual tool. Importantly our system exhibits better sensitivity and higher specificity than equivalent commercial software.
Conclusions: CoVaCS offers optimized pipelines integrating state of the art tools for variant calling and annotation for whole genome sequencing (WGS), whole-exome sequencing (WES) and target-gene sequencing (TGS) data. The system is currently hosted at Cineca, and offers the speed of a HPC computing facility, a crucial consideration when large numbers of samples must be analysed. Importantly, all the analyses are performed automatically allowing high reproducibility of the results. As such, we believe that CoVaCS can be a valuable tool for the analysis of human genome resequencing studies. CoVaCS is available at: https://bioinformatics.cineca.it/covacs .
Keywords: Consensus method; Graphical user interface; Variant annotation; Variant calling; Variant prioritization; Web server; Workflow.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The authors testify that this work was performed in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and have been approved by the Ethical, Legal and Social Implications (ELSI) Committee of the Istituto di Biomembrane Bioenergetica e Biotecnologie Molecolari, Consiglio Nazionale delle Ricerche, Bari, Italy (Ref. 2017/06/29).
Consent for publication
Not applicable
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- EPIGEN/Ministero dell'Istruzione, dell'Università e della Ricerca/International
- MTJU9H8: DICLIMAX: Strumentazione per diagnostica clinica basata su Next Generation sequencing di acidi nucleici,/Regione Puglia/International
- Bando di ricerca finalizzata e giovani ricercatori GR-2011-02347129/Ministero della Salute/International
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

