Bardoxolone Methyl Improves Kidney Function in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease Stage 4 and Type 2 Diabetes: Post-Hoc Analyses from Bardoxolone Methyl Evaluation in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease and Type 2 Diabetes Study
- PMID: 29402767
- PMCID: PMC5841134
- DOI: 10.1159/000486398
Bardoxolone Methyl Improves Kidney Function in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease Stage 4 and Type 2 Diabetes: Post-Hoc Analyses from Bardoxolone Methyl Evaluation in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease and Type 2 Diabetes Study
Abstract
Background: Increases in measured inulin clearance, measured creatinine clearance, and estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) have been observed with bardoxolone methyl in 7 studies enrolling approximately 2,600 patients with type 2 diabetes (T2D) and chronic kidney disease (CKD). The largest of these studies was Bardoxolone Methyl Evaluation in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease and Type 2 Diabetes (BEACON), a multinational, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 3 trial which enrolled patients with T2D and CKD stage 4. The BEACON trial was terminated after preliminary analyses showed that patients randomized to bardoxolone methyl experienced significantly higher rates of heart failure events. We performed post-hoc analyses to characterize changes in kidney function induced by bardoxolone methyl.
Methods: Patients in -BEACON (n = 2,185) were randomized 1: 1 to receive once-daily bardoxolone methyl (20 mg) or placebo. We compared the effects of bardoxolone methyl and placebo on a post-hoc composite renal endpoint consisting of ≥30% decline from baseline in eGFR, eGFR <15 mL/min/1.73 m2, and end-stage renal disease (ESRD) events (provision of dialysis or kidney transplantation).
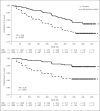
Results: Consistent with prior studies, patients randomized to bardoxolone methyl experienced mean increases in eGFR that were sustained through study week 48. Moreover, increases in eGFR from baseline were sustained 4 weeks after cessation of treatment. Patients randomized to bardoxolone methyl were significantly less likely to experience the composite renal endpoint (hazards ratio 0.48 [95% CI 0.36-0.64]; p < 0.0001).
Conclusions: Bardoxolone methyl preserves kidney function and may delay the onset of ESRD in patients with T2D and stage 4 CKD.
Keywords: Bardoxolone methyl; eGFR.
© 2018 The Author(s) Published by S. Karger AG, Basel.
Figures


References
-
- Wu QQ, Wang Y, Senitko M, Meyer C, Wigley WC, Ferguson DA, Grossman E, Chen J, Zhou XJ, Hartono J, Winterberg P, Chen B, Agarwal A, Lu CY. Bardoxolone Methyl (BARD) ameliorates ischemic AKI and increases expression of protective genes Nrf2, PPAR γ, and HO-1. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2011;300:F1180–F1192. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

