Genetic characteristics and phylogenetic analysis of three Chinese ethnic groups using the Huaxia Platinum System
- PMID: 29403025
- PMCID: PMC5799253
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-20871-7
Genetic characteristics and phylogenetic analysis of three Chinese ethnic groups using the Huaxia Platinum System
Abstract
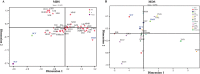
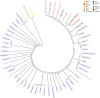
Short tandem repeats (STRs) are attractive to genetic applications like forensic, anthropological and population genetics studies. The Huaxia Platinum System was specifically developed to allow co-amplification and detection of all markers in the expanded CODIS core loci and the Chinese National Database. In this study, in continuation to our previous validation study, 568 unrelated individuals were firstly genotyped to investigate the effectiveness of this novel assay in 3 main ethnic groups of China (Han, Tibetan and Yi). The combined power of discrimination (CPD) were 0.9999999999999999999999999992, 0.999999999999999999999999992, 0.999999999999999999999999998, respectively, and the combined power of exclusion (CPE) were 0.9999999999, 0.999999995, 0.999999998, respectively. Next, genetic relationships along administrative and ethnic divisions were analyzed using pairwise genetic distances, multidimensional scaling (MDS), principal component analysis (PCA) and phylogenetic analysis. The Han ethnicity showed a high genetic homogeneity all across China, and significant genetic differences existed between Han groups and some minority groups, most prominently for the Tibetans, the Uyghurs, the Kazakhs, the Miaos, the Zhuangs and the Dais. Aforementioned results suggested that the Huaxia Platinum System is polymorphic and informative, which provides an efficient tool not only for human forensics, but also for population genetics studies.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Genetic polymorphism and phylogenetic differentiation of the Huaxia Platinum System in three Chinese minority ethnicities.Sci Rep. 2019 Mar 4;9(1):3371. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-39794-y. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 30833593 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic diversity and phylogenetic characteristics of Chinese Tibetan and Yi minority ethnic groups revealed by non-CODIS STR markers.Sci Rep. 2018 Apr 12;8(1):5895. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-24291-5. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29651125 Free PMC article.
-
Forensic features and phylogenetic analyses of Sichuan Han population via 23 autosomal STR loci included in the Huaxia Platinum System.Int J Legal Med. 2018 Jul;132(4):1079-1082. doi: 10.1007/s00414-017-1679-2. Epub 2017 Sep 5. Int J Legal Med. 2018. PMID: 28871330
-
Developmental Validation of the Huaxia Platinum System and application in 3 main ethnic groups of China.Sci Rep. 2016 Aug 8;6:31075. doi: 10.1038/srep31075. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27498550 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic Diversity and Phylogenetic Differentiation of Southwestern Chinese Han: a comprehensive and comparative analysis on 21 non-CODIS STRs.Sci Rep. 2017 Oct 23;7(1):13730. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-13190-w. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 29061987 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Genetic diversity and phylogenetic structure of four Tibeto-Burman-speaking populations in Tibetan-Yi corridor revealed by insertion/deletion polymorphisms.Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2020 Apr;8(4):e1140. doi: 10.1002/mgg3.1140. Epub 2020 Feb 3. Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2020. Retraction in: Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2024 Feb;12(2):e2371. doi: 10.1002/mgg3.2371. PMID: 32017463 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Genetic polymorphism and phylogenetic differentiation of the Huaxia Platinum System in three Chinese minority ethnicities.Sci Rep. 2019 Mar 4;9(1):3371. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-39794-y. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 30833593 Free PMC article.
-
New insights into the fine-scale history of western-eastern admixture of the northwestern Chinese population in the Hexi Corridor via genome-wide genetic legacy.Mol Genet Genomics. 2021 May;296(3):631-651. doi: 10.1007/s00438-021-01767-0. Epub 2021 Mar 1. Mol Genet Genomics. 2021. PMID: 33650010
-
Are ethnic differences, urinary iodine status, lead and cadmium exposure associated with thyroid autoimmunity and hypothyroid status? A cross-sectional study.BMJ Open. 2022 Feb 17;12(2):e056909. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2021-056909. BMJ Open. 2022. PMID: 35177462 Free PMC article.
-
Myopia prevalence and ocular biometry: a cross-sectional study among minority versus Han schoolchildren in Xinjiang Uygur autonomous region, China.Eye (Lond). 2022 Oct;36(10):2034-2043. doi: 10.1038/s41433-021-01506-0. Epub 2021 Aug 19. Eye (Lond). 2022. PMID: 34413492 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Butler JM, Hill CR. Biology and Genetics of New Autosomal STR Loci Useful for Forensic DNA Analysis. Forensic Sci. Rev. 2012;24:15–26. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

