Magnetic immunoassay using CdSe/ZnS quantum dots as fluorescent probes to detect the level of DNA methyltransferase 1 in human serum sample
- PMID: 29403274
- PMCID: PMC5777376
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S152618
Magnetic immunoassay using CdSe/ZnS quantum dots as fluorescent probes to detect the level of DNA methyltransferase 1 in human serum sample
Abstract
Background: DNA methyltransferase 1 (DNMT1), a dominant enzyme responsible for the transfer of a methyl group from the universal methyl donor to the 5-position of cytosine residues in DNA, is essential for mammalian development and closely related to cancer and a variety of age-related chronic diseases. DNMT1 has become a useful biomarker in early disease diagnosis and a potential therapeutic target in cancer therapy and drug development. However, till now, most of the studies on DNA methyltransferase (MTase) detection have focused on the prokaryote MTase and its activity.
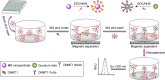
Methods: A magnetic fluorescence-linked immunosorbent assay (FLISA) using CdSe/ZnS quantum dots as fluorescent probes was proposed for the rapid and sensitive detection of the DNMT1 level in this study. Key factors that affect the precision and accuracy of the determination of DNMT1 were optimized.
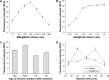
Results: Under the optimal conditions, the limit of detection was 0.1 ng/mL, the linear range was 0.1-1,500 ng/mL, the recovery was 91.67%-106.50%, and the relative standard deviations of intra- and inter-assays were respectively 5.45%-11.29% and 7.03%-11.25%. The cross-reactivity rates with DNA methyltransferases 3a and 3b were only 4.0% and 9.4%, respectively. Furthermore, FLISA was successfully used to detect the levels of DNMT1 in human serum samples, and compared with commercial enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) kits. The results revealed that there was a good correlation between FLISA and commercial ELISA kits (correlation coefficient r=0.866, p=0.001). The linear scope of FLISA was broader than ELISA, and the measurement time was much shorter than ELISA kits.
Conclusion: These indicated that the proposed FLISA method was sensitive and high throughput and can quickly screen the level of DNMT1 in serum samples.
Keywords: DNA methyltransferase 1; fluorescence immunoassay; high throughput; magnetic carboxyl beads; quantum dots; serum sample.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Highly sensitive and accurate detection of C-reactive protein by CdSe/ZnS quantum dot-based fluorescence-linked immunosorbent assay.J Nanobiotechnology. 2017 May 2;15(1):35. doi: 10.1186/s12951-017-0267-4. J Nanobiotechnology. 2017. PMID: 28464873 Free PMC article.
-
Development of Quantum Dots-Labeled Antibody Fluorescence Immunoassays for the Detection of Morphine.J Agric Food Chem. 2017 Feb 15;65(6):1290-1295. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.6b05305. Epub 2017 Feb 6. J Agric Food Chem. 2017. PMID: 28132500
-
A Novel Fluoroimmunoassay for Detecting Ruscogenin with Monoclonal Antibodies Conjugated with CdSe/ZnS Quantum Dots.Molecules. 2017 Jul 26;22(8):1250. doi: 10.3390/molecules22081250. Molecules. 2017. PMID: 28933731 Free PMC article.
-
Stability and fluorescence quantum yield of CdSe-ZnS quantum dots--influence of the thickness of the ZnS shell.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2008;1130:235-41. doi: 10.1196/annals.1430.021. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2008. PMID: 18596353 Review.
-
Recent advances in quantum dot-based fluorescence-linked immunosorbent assays.Nanoscale. 2023 Mar 23;15(12):5560-5578. doi: 10.1039/d2nr07247e. Nanoscale. 2023. PMID: 36866747 Review.
Cited by
-
Multiplexed Nanobiosensors: Current Trends in Early Diagnostics.Sensors (Basel). 2020 Dec 2;20(23):6890. doi: 10.3390/s20236890. Sensors (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33276535 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hay SI, Jayaraman SP, Manzano AGC, et al. GBD 2015 Risk Factors Collaborators Global, regional, and national comparative risk assessment of 79 behavioural, environmental and occupational, and metabolic risks or clusters of risks, 1990–2015 a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015. Lancet. 2017;389(10064):E1.
-
- Qiu J. Epigenetics: unfinished symphony. Nature. 2006;441(7090):143–145. - PubMed
-
- Jones PA, Baylin SB. The fundamental role of epigenetic events in cancer. Nat Rev Genet. 2002;3(6):415–428. - PubMed
-
- Schübeler D. Function and information content of DNA methylation. Nature. 2015;517(7534):321–326. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

