Upregulated Heat Shock Proteins After Hyperthermic Chemotherapy Point to Induced Cell Survival Mechanisms in Affected Tumor Cells From Peritoneal Carcinomatosis
- PMID: 29403306
- PMCID: PMC5791678
- DOI: 10.1177/1179064417730559
Upregulated Heat Shock Proteins After Hyperthermic Chemotherapy Point to Induced Cell Survival Mechanisms in Affected Tumor Cells From Peritoneal Carcinomatosis
Abstract
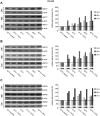
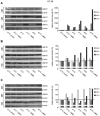
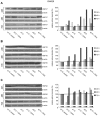
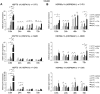
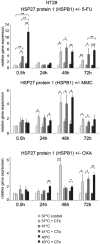
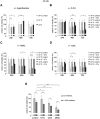
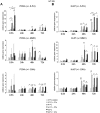
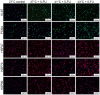
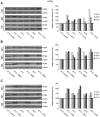
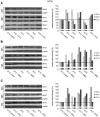
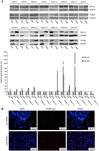
In patients with peritoneal carcinomatosis cytoreductive surgery combined with hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy (HIPEC) represents a promising treatment strategy. Here, we studied the role of hyperthermic chemotherapy on heat shock protein (HSP) expression and induction of tumor cell death and survival. HSP27, HSP70, and HSP90 combined with effects on tumor cell proliferation and chemosensitivity were analyzed in human colon cancer. Hyperthermic chemotherapy resulted in significant HSP27/HSP70 and HSP90 gene/protein overexpression in analyzed HT-29/SW480/SW620 colon cancer cells and peritoneal metastases from patients displaying amplified expression of proliferation markers, proliferating cell nuclear antigen and antiapoptotic protein Bcl-xL. Moreover, functionally increased chemoresistance against 5-fluorouracil/mitomycin C and oxaliplatin after hyperthermic chemotherapy points to induced survival mechanisms in cancer cells. In conclusion, the results indicate that intracellular HSP-associated antiapoptotic and proliferative effects after hyperthermic chemotherapy negatively influence beneficial effects of hyperthermic chemotherapy-induced cell death. Therefore, blocking HSPs could be a promising strategy to further improve the rate of tumor cell death and outcome of patients undergoing HIPEC therapy.
Keywords: Heat shock proteins; apoptosis; chemoresistance; hyperthermia; hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy; peritoneal carcinomatosis.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of conflicting interests:The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures
References
-
- Elias D, Lefevre JH, Chevalier J, et al. Complete cytoreductive surgery plus intraperitoneal chemohyperthermia with oxaliplatin for peritoneal carcinomatosis of colorectal origin. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27:681–685. - PubMed
-
- Sugarbaker PH, Yonemura Y. Clinical pathway for the management of resectable gastric cancer with peritoneal seeding: best palliation with a ray of hope for cure. Oncology. 2000;58:96–107. - PubMed
-
- Spiliotis JD. Peritoneal carcinomatosis cytoreductive surgery and HIPEC: a ray of hope for cure. Hepatogastroenterology. 2010;57:1173–1177. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

